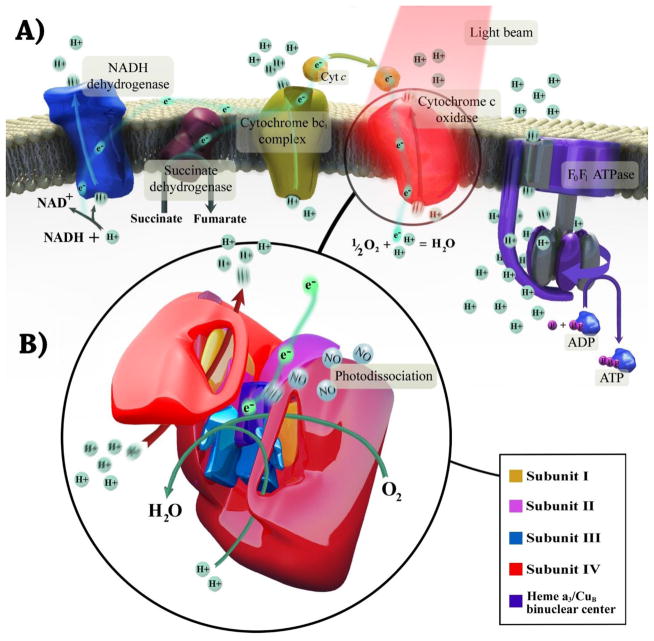
Fig. 1. Mechanism of photobiomodulation therapy in mitochondria.
(A) The flow of electrons and protons through the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Photobiomodulation stimulates cytochrome c oxidase, improves its catalytic activity, and elevates ATP synthesis. All these results in enhancement of neuronal respiration and metabolic capacity. (B) The structure of cytochrome c oxidase and electrons path through its subunits. The complex contains two copper centers as well as two heme prosthetic groups. Photobiomodulation may dissociate nitric oxide from binuclear center (a3/CuB), allowing oxygen to return, and facilitates electron transfer and increases proton gradient.