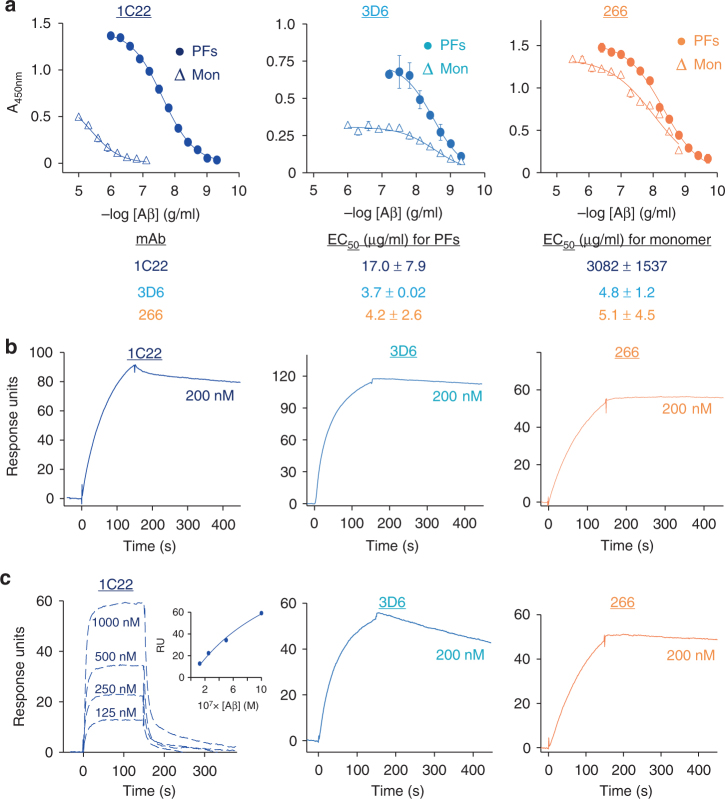
Fig. 2.
Surface-immobilized 1C22 mAb preferentially binds to PFs in solution. a mAbs 1C22, 3D6, and 266 were immobilized on the wells of microtiter plates and allowed to bind solution-phase protofibrils (PFs) and Aβ monomers (Mon). Antibody binding curves were sigmoidally fit and used to determine the concentration of antibody that gave half-maximal binding, EC50. When error bars are not visible they are smaller than the size of the symbol. Values in the table are in μg/ml and are the average ± SD of each condition analyzed in triplicate. Antibodies were immobilized on CM5 chips and solution-phase b PFs, or c Mon added. The molar concentration of Aβ monomers and PFs (wrt to Aβ monomer content) used is indicated on each sensogram. Except for Aβ monomer binding by 1C22, sensograms for mAb binding to Aβ monomers were fit to a 1:1 langmuir binding model. Sensograms for 1C22 binding to Aβ monomers were fit to steady state analysis. The inset in c panel 1 is a plot of response units (RU) at steady state for Aβ monomers binding to chip-immobilized 1C22. The apparent binding constant (KAPP) of mAbs for PFs are: 1C22 < 1 nM; 3D6 < 1 nM; 266 < 1 nM, and the binding constants (KD) for Mon are: 1C22 = 1100 ± 500 nM; 3D6 = 7.9 ± 0.16 nM; and 266 = 2.1 ± 1.8 nM