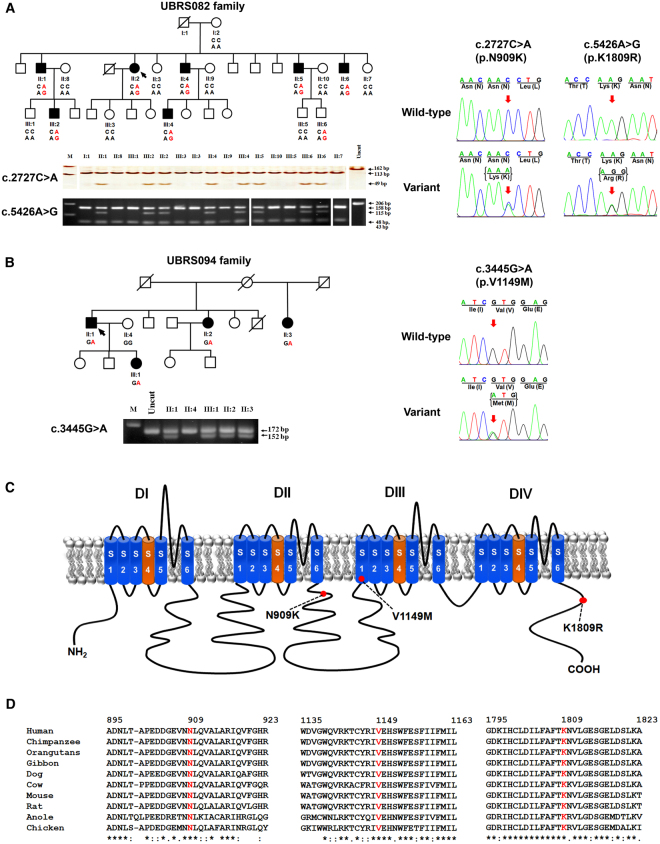
Figure 1.
Segregation analysis of KSD and SCN10A variations in two affected families, schematic diagram of the NaV1.8 α subunit structure, and multiple amino-acid sequence alignment of NaV1.8 α subunit. (A) Co-segregation of KSD and two SCN10A variations [c.2727 C > A (p.N909K), and c.5426 A > G (p.K1809R)] in the UBRS082 family, and sequencing profile of the variations. One member (III:6), aged 15 years, carried the variations without KSD; this may be explained by the late-onset nature (>25 years) of the disease. (B) Co-segregation of KSD and SCN10A variation [c.3445 G > A (p.V1149M)] in the UBRS094 family, and sequencing profiles of the variations. (C) Schematic diagram of the NaV1.8 α subunit of voltage-gated sodium channel and distribution of mutations. The red dots indicate the approximate locations of the three identified variations (p.N909K, p.V1149M, and p.K1809R). (D) Multiple amino-acid sequence alignments of NaV1.8 α subunit from six vertebrate species in three regions where the variations (p.N909K, p.V1149M, and p.K1809R) were identified, which indicate that asparagine (N) at position 909, valine (V) at position 1149, and lysine (K) at position 1809 are highly conserved. Images of the gels cropped from different parts of the same gel, or from different gels were separated by white space. The full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. S8.