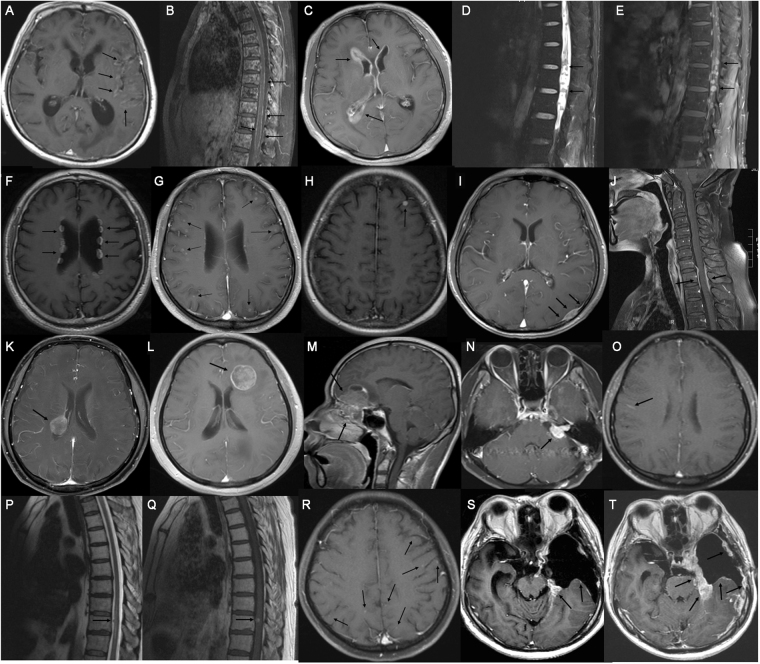
Figure 1.
Neuroimaging findings. (A) Diffuse pial enhancement in brain sulcus, especially the left temporal lobe. (B) Diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement in vertebral canal. (C) Enhancement of subependyma in the bilateral ventricles. (D) Multiple nodular lesions in spinal canal in T2-weighted sequences. (E) Obvious enhancement in contrast enhanced T1-weighted sequences. (F) Multiple nodular lesions with enhancement in the wall of lateral ventricles. (G) Enhancement of metastatic nodules in cerebral cortex. (H) Metastatic lesion in subarachnoid space. (I) Dural enhancement in left occiput and rat-tail sign were observed. (J) Dural enhancement in local spinal canal. (K) Metastatic lesion in the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle. (L) Metastatic lesion correlated to the anterior horn of the left lateral ventricle. (M) The rhabdomyosarcoma of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity invaded across the bottom of anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe. (N) The enhancement of auditory and facial nerves at the left cerebellopontine angle. (O) Fuzzy pial enhancement presented at the sulcus and gyrus. (P,Q) A Lesion of implantation metastasis on the surface of spinal cord. (R) The occult metastatic nodules in cerebral cortex. (S) Subdural hydroma at the left tempus. Slight enhancement of the local dura mater. (T) One month later, it showed worse subdural effusion and diffusely dural thickening and enhancement.