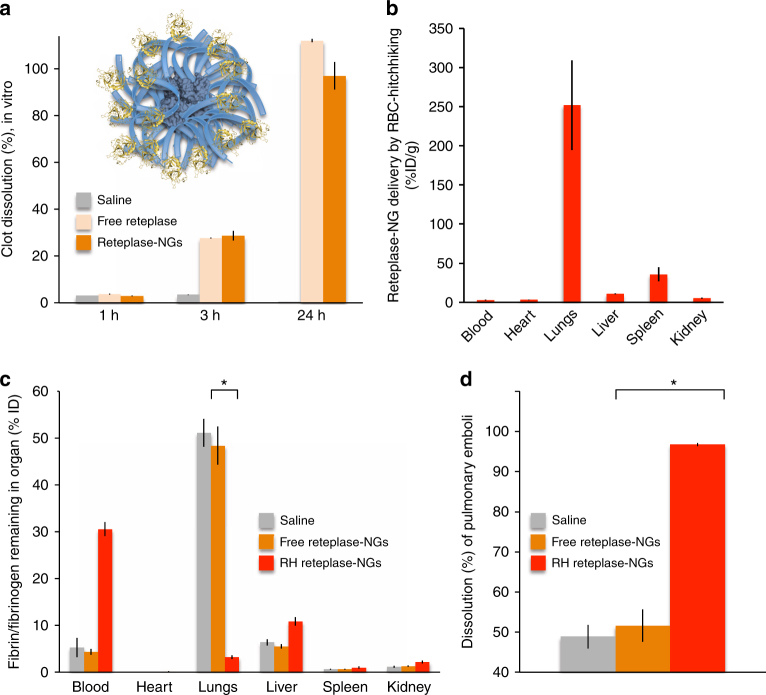
Fig. 6.
RH effectively delivers therapeutic cargo to ameliorate a model of pulmonary embolism. a Inset, schematic of nanogels (NGs) with thrombolytic enzyme reteplase (gold) conjugated to the dextran (blue) shell. The bar graph shows the degree to which reteplase-NGs, free reteplase, or saline dissolve preformed fibrin clots in vitro. Reteplase conditions contained 4 nM of reteplase, with reteplase concentration in reteplase-NGs quantified by reteplase-NG coupling efficiency. b Biodistribution of RH reteplase-NGs at 1 h after injection, showing high lung uptake. c All mice were intravenously injected with ~1–5 micron diameter fibrin clot emboli (I-125-labeled). Mice were also treated with either saline, free reteplase-NGs, or RH reteplase-NGs at 12 micrograms reteplase per mouse. The amount of I-125-labeled fibrin/fibrinogen remaining in each organ at 1 h post injection is quantified. d Degree to which initially injected emboli were cleared from the lungs. For all plots in this figure, each data point represents mean ± s.e.m (n = 4). *P < 0.001, non-paired, two-tailed t-test