Figure 3.
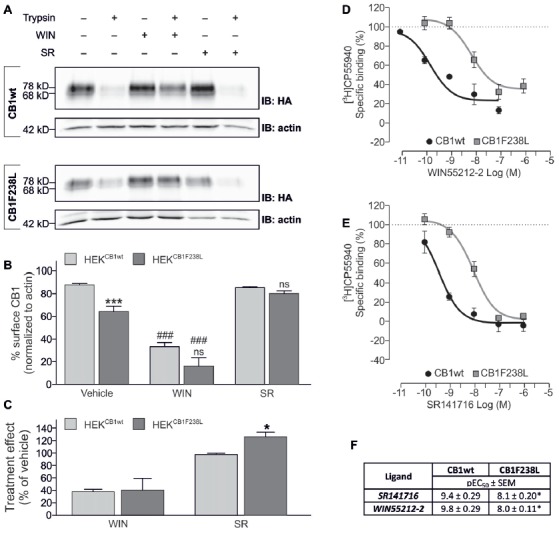
Effect of WIN-55212-2 and SR141716 on surface expression of HA-CB1F238L compared to HA-CB1wt. (A) HEK293 cells stably expressing HA-CB1wt or HA-CB1F238L were treated either with vehicle, 100 nM WIN-55212-2 or 100 nM SR141716 for 45 min. Surface expression was analyzed by a trypsin protection assay. (B) Strong internalization after WIN-55212-2 treatment was observed for both receptors. SR141716 treatment rescued surface expression of CB1F238L receptor back to wild-type levels. Surface HA-CB1 was calculated and expressed as percent of total HA-CB1 as described in “Materials and Methods” section. (Two way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of n = 4 independent experiments. ***p < 0.001; n.s., p > 0.05 vs. wild-type; ###p < 0.001 vs. vehicle). (C) The effect of SR141716 on surface expression is significantly increased for CB1F238L receptor (Student’s t-test between genotypes. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of n = 4 independent experiments. *p < 0.05). Competition binding experiments with radiolabeled CB1 receptor agonist [3H]CP55940 showed that the F238L mutation causes a decrease in the affinity of CB1 receptor (D) for the agonist WIN55212-2 and (E) for the inverse agonist SR141716. (F) In competition binding experiments with [3H]CP-55940 the CB1F238L receptor showed significantly reduced affinity for WIN-55212-2 as well as for SR141716. (Student’s t-test of pEC50. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of n = 3–8 independent experiments. *p < 0.05).
