Figure 3.
FORMIN4 Contributes to Defense and Actin Organization at the Site of Immunity
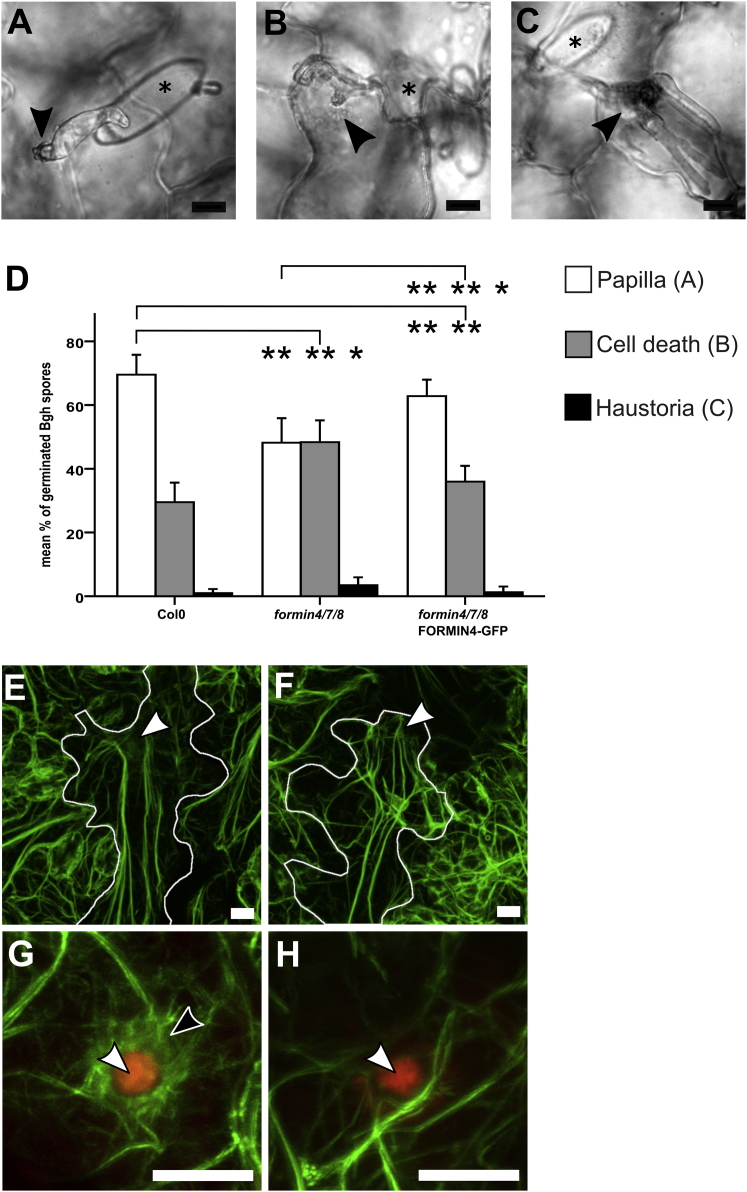
(A) At 48 hr after infection, most wild-type A. thaliana epidermal cells responding to Bgh appressoria have formed a CWA (indicated by arrowhead).
(B) A proportion of cells enter programmed cell death, identified by absence of cytoplasmic streaming, aggregation of the cytoplasm, and pigmentation of the cell.
(C) A small minority of cells contain fungal haustoria. Asterisk in (A)–(C) indicates conidia.
(D) Comparison of the frequency of responses in different genotypes. Compared to wild-type (Col-0), formin4/7/8 plants show increased rates of cell death and haustoria formation upon Bgh challenge. Expression of FORMIN4-GFP in the formin4/7/8 genetic background fully rescues mutant susceptibility to haustoria formation and reduces cell death rates near to wild-type levels. Single asterisks indicate p values less than 0.05; double asterisks indicate p values less than 0.01 (evaluated by pairwise comparison applying Student’s t test). Error bars show SD of at least three biological repeats (minimum of 22 leaves per genotype). See also Figure S3.
(E) Wild-type cells expressing actin-binding GFP-Lifeact show a cable network that interacts with the region containing the CWA (labeled using a white arrowhead; white lines mark the boundary of the affected epidermal cell).
(F) The CWA (position indicated by white arrowhead) maintains interactions with the actin cable network in mutant formin4/7/8 plants expressing GFP-Lifeact.
(G) GFP-Lifeact-labeled filaments (green) surrounding wild-type CWAs (red autofluorescence and white arrowhead). Black arrowhead indicates coronal (peri-CWA) actin network.
(H) GFP-Lifeact labeling filamentous actin in the area surrounding a mutant CWA.
The scale bars represent 10 μm.