Figure 10.
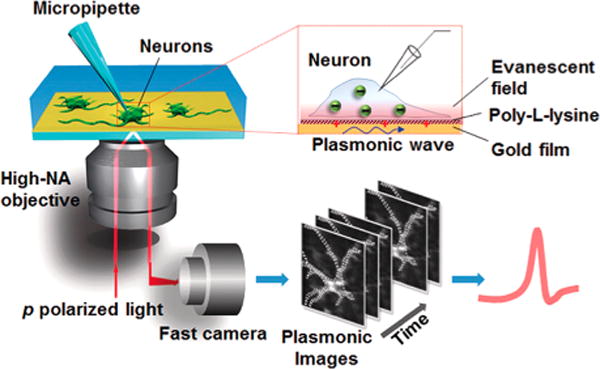
Setup of plasmonic imaging of action potential in neurons. A p-polarized light beam is directed onto a gold-coated glass coverslip through an oil immersion objective to excited plasmons on the gold surface, which is imaged optically with a fast camera. Neurons are cultured on the poly-L-lysine-coated gold surface, and a micropipette is patched on one neuron to trigger action potential that is recorded with both the patch clamp electronics and plasmonic imaging. When an action potential spike is triggered, ions move in and out of the neuron via the ion channels, creating a transient charge near the gold surface, which affects surface plasmons on the gold film, which is imaged optically with P-EIM. Reproduced from Plasmonic-Based Electrochemical Impedance Imaging of Electrical Activities in Single Cells, Liu, X. W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Gao, M.; Wu, J.; Tao, N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Vol. 56, Issue 30 (ref 222). Copyright 2017 Wiley.
