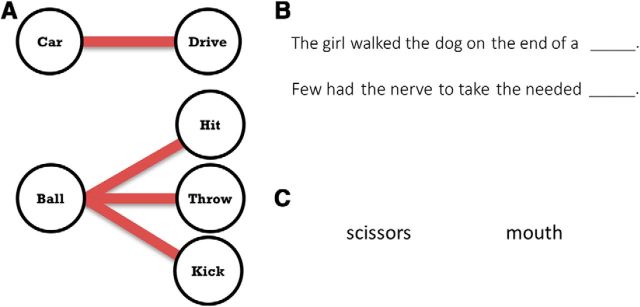
Figure 2.
Overview of tasks. A, High verbal selection demands are introduced when a cuing noun is associated with multiple appropriate words (here, verbs). Top, Example of a stimulus-response pairing with low selection demands. Bottom, Stimulus–response pairing with high selection demands. B, Example items from the sentence completion task. Participants were asked to provide an appropriate noun at the end of the sentence. Top, This item has a low selection demand because “leash” is easily and dominantly recalled in the context of this sentence. Bottom, This item has a high selection demand because several alternate words may be appropriate to complete the sentence. C, Example items from the verb generation task. Participants were asked to provide an appropriate verb associated with the noun. Left, This item has a low selection demand because “cut” is the most dominant verb associated with “scissors.” Right, This item has a high selection demand because several verbs are highly associated with the mouth, such as “eat,” “talk,” and “kiss.”