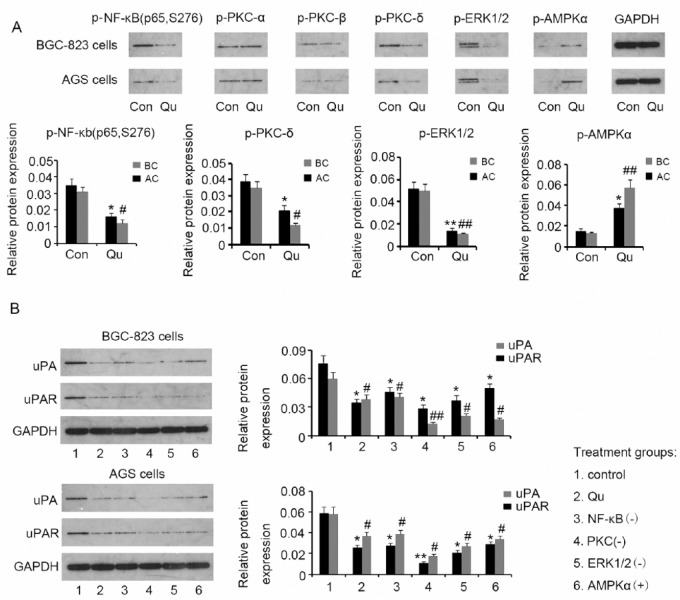
Figure 6.
Suppression of the uPA/uPAR system by Qu may be mediated by NF-κb, PKC-δ, ERK1/2, and AMPKα. (A) Phosphorylation levels of NF-κb (p65), PKC-α, PKC-β, PKC-δ, ERK1/2, and AMPKα were evaluated in BGC823 and AGS cells by Western blotting, after treatment with 10 μM Qu for 72 hours. Qu treatment was associated with inhibition of NF-κb, PKC-δ, and ERK1/2 activities and with AMPKα activation. (B) Specific inhibitors of NF-κb (p65), PKC, and ERK1/2, as well as activators of AMPKα were used to assess their roles in uPA and uPAR regulation. BGC823 and AGS cells were incubated with 9 μM JSH-23, 10 nM Go6983, 12 μM SCH772984, or 4.5 μM A-769662 for 72 hours. Similar to Qu, specific inhibitors of NF-κb, PKC, and ERK1/2, and an AMPKα activator suppressed uPA and uPAR expression in GC cells. Bars representing the average of data from 3 independent tests. *P < .05, **P < .01, #P < .05, ##P < .01 versus control group. Qu, quercetin; uPA, urokinase plasminogen activator; uPAR, uPA receptor; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; NF-κb, nuclear factor-κb; PKC, protein kinase C; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; AMPKα, adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase α; NF-κb(−), NF-κb inhibition with the inhibitor; PKC(−), PKC inhibition with the inhibitor; ERK1/2(−), ERK1/2 inhibition with the inhibitor; AMPKα(+), AMPKα activation with the activator.