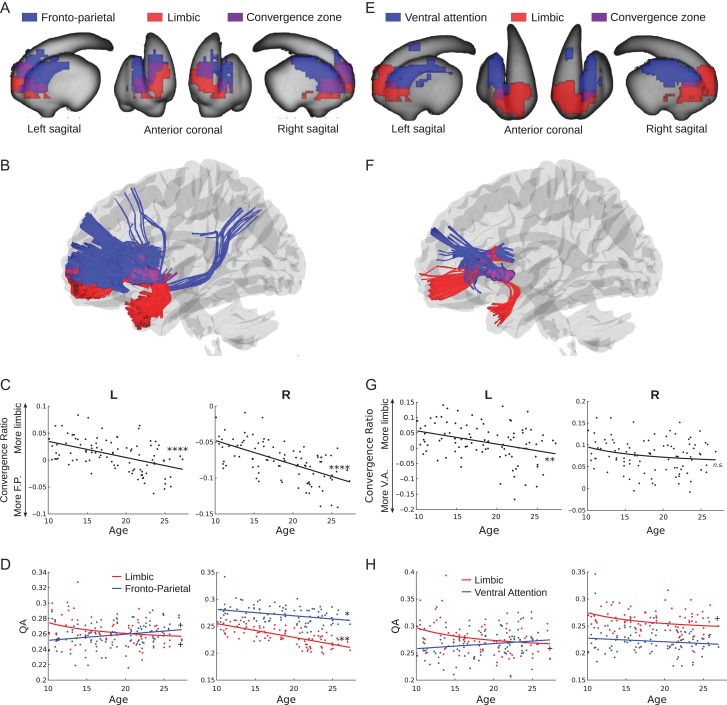
Figure 3.
Affective/cognitive convergence assessed using quantitative anisotropy. (A) Limbic (red) and fronto-parietal (blue) corticostriatal fiber tracking striatal endpoints overlaid on the surface of the striatum. The convergent zone is colored in purple. (B) Fiber tracts connecting the limbic (red) and fronto-parietal (blue) cortical regions of interest to the striatal convergent zone from (A). (C) The convergence ratio significantly decreased with age throughout adolescence in both hemispheres (Table 1). (D) The individual maturational trajectories of limbic and fronto-parietal projections to the convergent zone. (E) Limbic (red) and ventral attention (blue) corticostriatal fiber tracking striatal endpoints overlaid on the surface of the striatum. The convergent zone is colored in purple. (F) Fiber tracts connecting the limbic (red) and ventral attention (blue) cortical regions of interest to the striatal convergent zone from (E). (G) The convergence bias significantly decreased with age throughout adolescence in the right hemisphere only. (H) The individual maturational trajectories of limbic and ventral attention projections to the convergent zone. + P < 0.05 uncorrected; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 Bonferroni corrected.