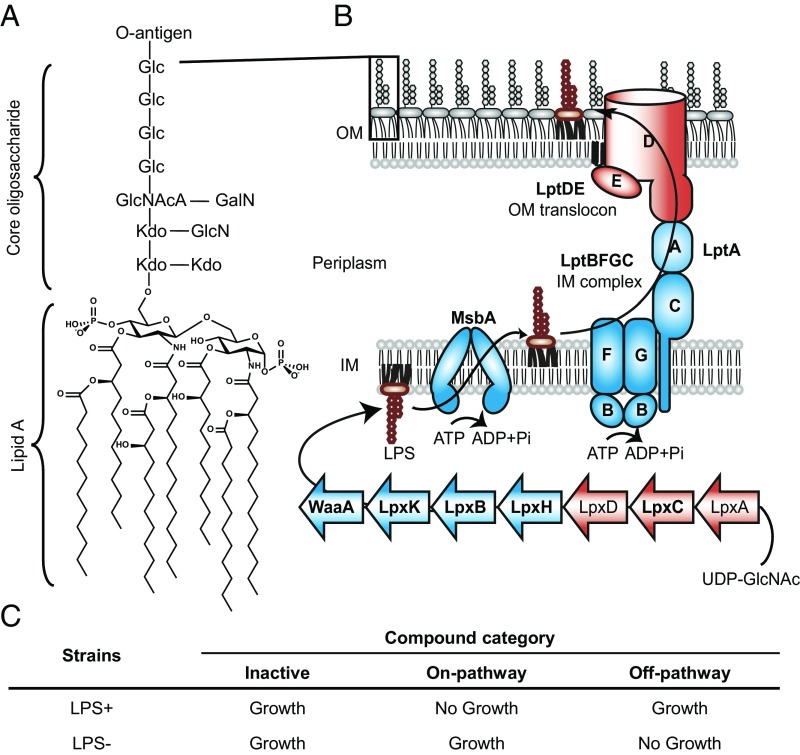
Fig. 1.
Certain genes in the LPS biogenesis pathway of Acinetobacter are conditionally essential. (A) LPS is a complex glycolipid and consists of hepta-acylated lipid A (in Acinetobacter), core oligosaccharides, and O-antigen. (B) LPS biogenesis starts with biosynthesis in the cytoplasm and transport of LPS from the inner membrane to the outer membrane, followed by assembly at the cell surface. Nonessential genes initiating lipid A biosynthesis (lpxA/C/D, red) and at the final step of the transport process (lptD/E, red), along with conditionally essential intermediate steps (lpxH/B/K, waaA, msbA, and lptA/B/C/F/G, blue) are indicated. Genes (bold) were experimentally verified in A. baylyi (SI Appendix, Fig. S1). The specific acylation pattern and core sugar composition of LPS are based on published reports (45, 46). O-antigen–related proteins are omitted for simplicity. Abbreviations: GalN, galactosamine; Glc, glucose; GlcN, glucosamine; GlcNAcA, 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-glucopyranosyluronic acid; Kdo, 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulopyranosonic acid. (C) LPS biogenesis inhibitors are distinguished from off-pathway or inactive compounds based on distinct sensitivities of strains with and without LPS.