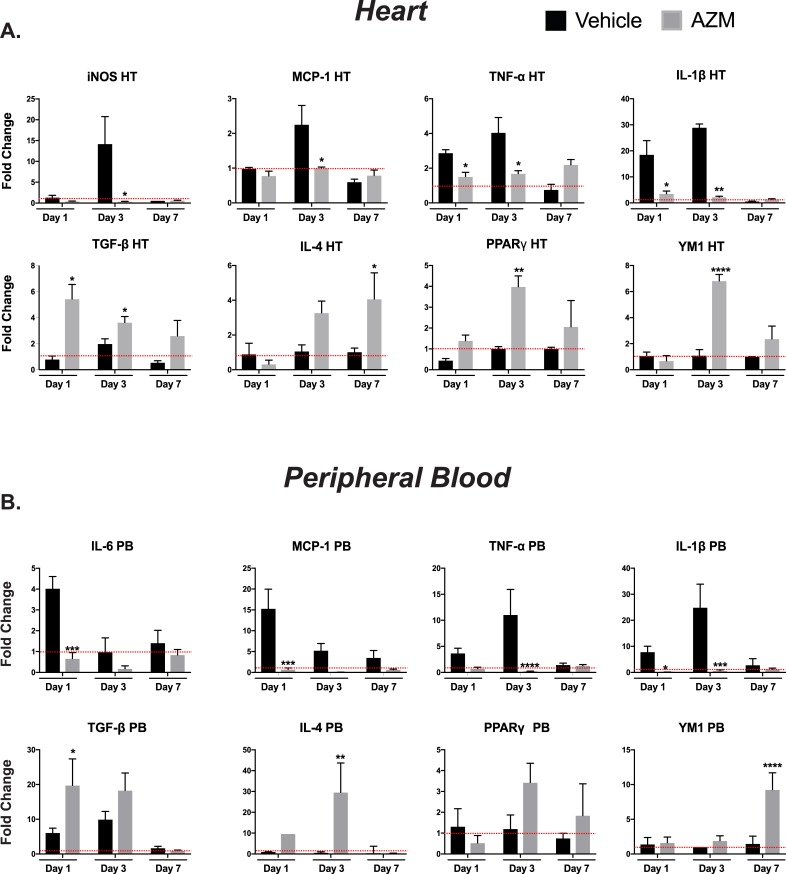
Fig 4. AZM treatment exerts immunomodulatory effects on cytokines expression following MI.
mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in HT (Panel A) and PB (Panel B), demonstrate significant reduction in gene expression of these cytokines in the early inflammatory phase following injury with AZM therapy compared to vehicle controls (red line demarcates the level of gene expression in sham operated mice). The mRNA expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines is augmented with AZM therapy compared to vehicle control (n = 4 mice/group/time point, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and **** P<0.0001 compared to vehicle controls). Data presented as mean ± SEM. AZM, azithromycin; HT, heart; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-4, interleukin 4; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; PB, peripheral blood; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; TGF-1β, tissue growth factor 1 beta; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; YM1 (Chil3), chitinase-like 3.