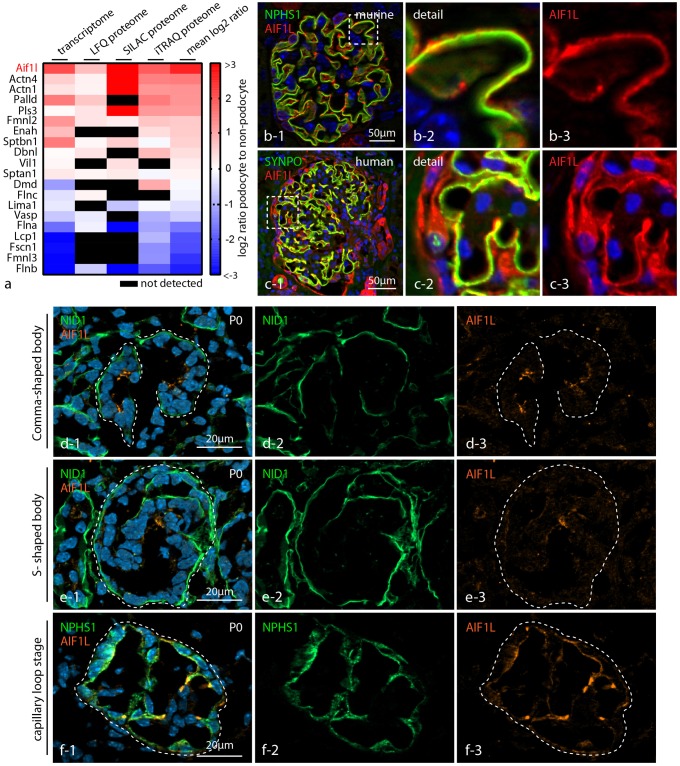
Fig 1. AIF1L is specifically expressed in podocytes.
(a) Cross-analysis of transcriptome as well as proteome data sets for actin bundling proteins (unlabeled and quantitative—see for details Materials and methods sections) revealed highly selective expression of AIF1L in podocytes compared to non-podocyte glomerular cells. (b-c) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy demonstrated pronounced co-localization between AIF1L and the podocyte compartment visualized by the specific slit diaphragm component NEPHRIN (NPHS1) or the podocyte specific cytoskeleton protein SYNPO (note expression of AIF1L also in tubular compartments and parietal epithelial glomerular cells in human kidney sections). Here, AIF1L localizes prominently to the basal compartment of podocytes as demonstrated by linear co-localization with NEPHRIN and SYNPO. Of note, AIF1L is also detectable in the whole podocyte cell (note divergences in cytoplasmic localization between mice and human podocytes). (d-f) Immunofluorescence microscopy on different glomerular maturation stages in a p0 wild type murine kidney section: AIF1L is present throughout all stages of glomerular maturation (Nidogen (NID1) was used as a marker for visualizing basement membrane structures, NPHS1 for the podocyte compartment).