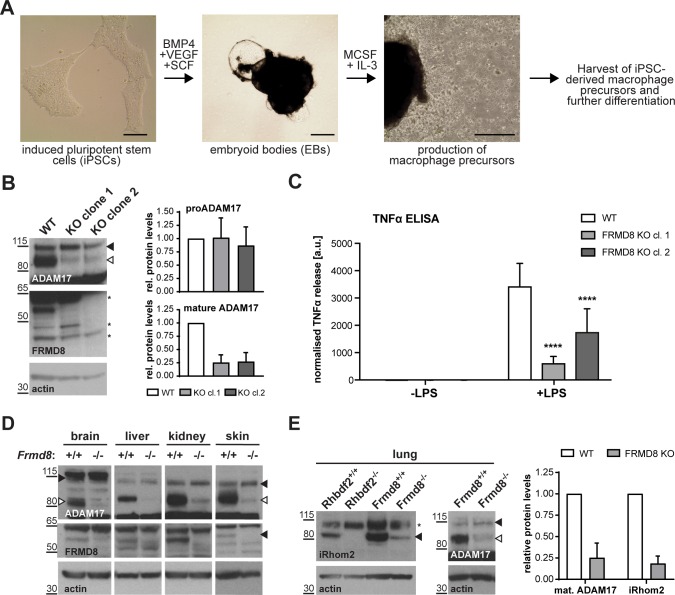
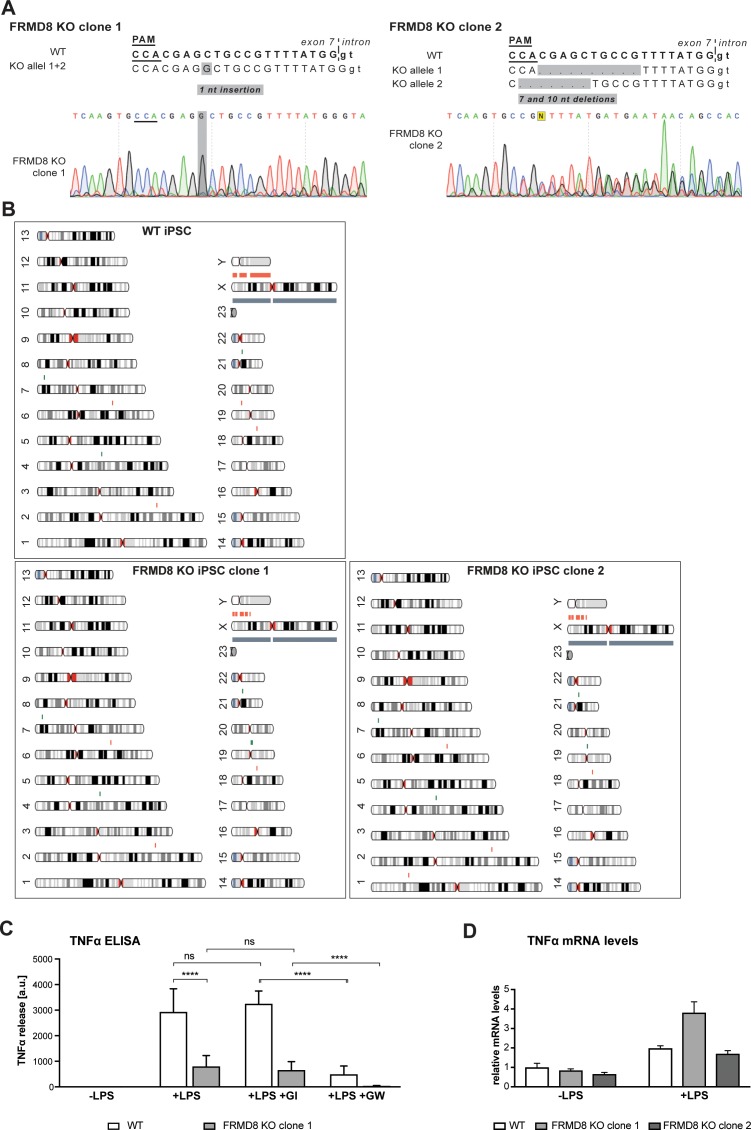
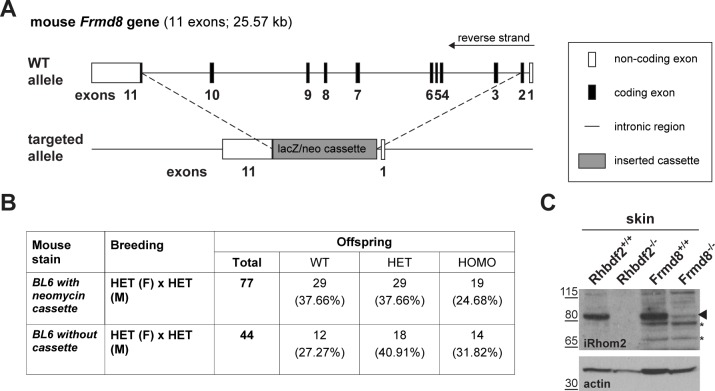
Figure 9. FRMD8 is required for iRhom2/TACE regulation in human iPSC-derived macrophages and mice .
(A) Schematic representation of the differentiation protocol of iPSCs into macrophages based on (van Wilgenburg et al., 2013). Scale bars = 10 μm. (B) Lysates of iPSC-derived macrophages (on day seven after harvest from EBs) were immunoblotted for ADAM17, FRMD8, and actin. Western blots from three experiments were quantified using ImageJ with actin serving as the loading control. (C) 25,000 iPSC-derived macrophages were either left unstimulated or stimulated with 50 ng/ml LPS for 4 hr. TNFα concentration in the cell supernatants was measured by ELISA and then normalised to the protein concentration in macrophage cell lysates to adjust the cytokine release for potential differences in cell numbers. Each experiment was performed in biological triplicates. Data from three independent experiments were statistically analysed using a Mann-Whitney test; ***=p value<0.001; ****=p value<0.0001. (D, E) Lysates from tissues derived from Frmd8-/- or Rhbdf2-/- and their wild-type littermates were immunoblotted for ADAM17, FRMD8, iRhom2 and actin. Blots from three experiments using three different littermates of Frmd8-/- and Frmd8+/+ mice were quantified using ImageJ with actin serving as the loading control.