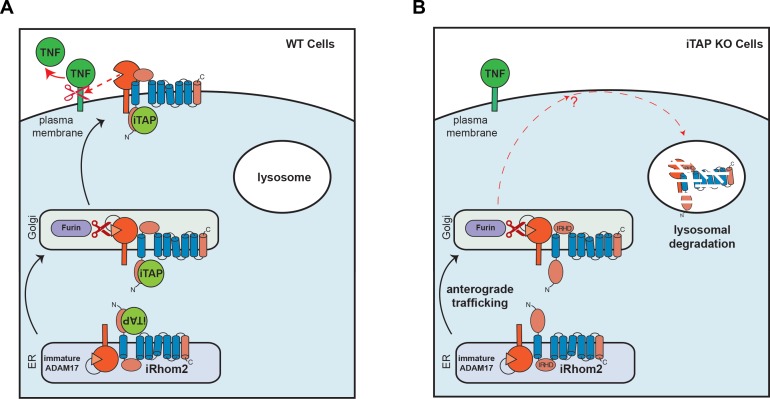
Figure 8. Schematic model showing regulation of the cell surface stability of the sheddase complex by iTAP.
(A). In WT cells the iRhom2/TACE sheddase complex successfully transits from the ER to the Golgi apparatus, where TACE undergoes maturation (prodomain removal). The sheddase complex then traffics to the cell surface, where TACE cleaves it substrates (e.g. TNF, EGFR ligands), enabling their release for signaling. iTAP, which loads onto the sheddase complex in the ER, remains associated with the sheddase complex and ensures the stability of the complex on the cell surface, promoting the cleavage of TACE substrates. (B). By contrast, in iTAP KO cells, the sheddase complex is aberrantly sorted to the lysosome, where iRhom2 and mature TACE are degraded. As a result, no TACE substrates are released for signaling. The dotted arrows indicate a putative itinerary taken by the sheddase complex in iTAP KO cells. The sheddase complex may be destabilized on the cell surface: aberrantly targeted for endocytosis and shunted to the lysosome. Alternatively, the sheddase complex may be endocytosed from the cell surface at the normal rate, but loss of iTAP may result in a defect in recycling the complex back to the cell surface, favouring delivery to the lysosome.