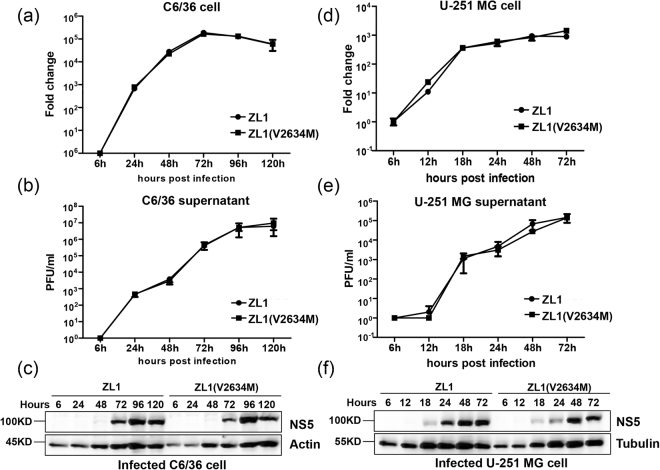
Figure 6.
Comparing the replication and infectivity of ZL1(V2634M) with wild type ZL1 in C6/36 cells and U-251 MG cells. (a/b) Comparison of the replication and virus production of wild type ZL1 with mutated ZL1(V2634M) in C6/36 cells. C6/36 cells were infected with ZL1or ZL1(V2634M) at MOI = 0.01, the cell pellet and supernatant were collected at 6, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120 hours post infection. Intracellular ZIKV RNA copies and virus titer in cell culture supernatant were detected by q-RT-PCR and plaque assay, respectively. Data represent the means of three independent assays; Error bars represent standard deviations from the means. (c) Western blot analysis of viral protein in infected C6/36 cells. Cell pellets harvested at hours 6, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120 post infection were detected by using home-made polyclonal antibody against NS5. (d/e) Comparison of the replication and virus production of ZL1 and ZL1(V2634M) in U-251 MG cells. U-251 MG cells were infected with ZL1 or ZL1(V2634M) at MOI = 0.01, the cell pellet and supernatant were collected at 6, 12, 18, 24, 48, 72 hours post infection. Intracellular ZIKV RNA copies and virus titer in cell culture supernatants were detected by q-RT-PCR and plaque assay, respectively. Data represent the means of three independent assays; Error bars represent standard deviations from the means. (f) Western blot analysis of viral protein in infected U-251 MG cells. Cell pellets harvested at hours 6, 12, 18, 24, 48, 72 post infection were detected by using home-made polyclonal antibody against NS5.