Fig. 2.
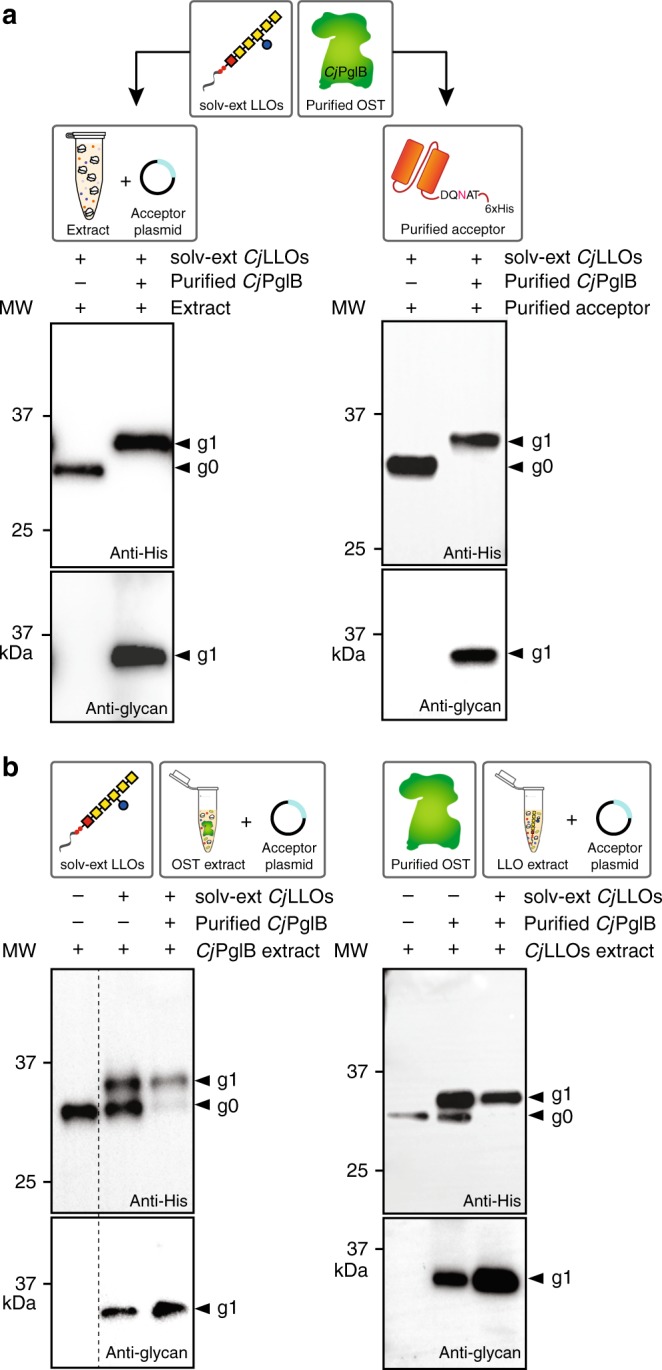
Extract from glyco-optimized chassis strain supports CFGpS. a (left) Western blot analysis of scFv13-R4DQNAT produced by crude CLM24 extract supplemented with purified CjPglB and organic solvent-extracted (solv-ext) CjLLOs, and primed with plasmid pJL1-scFv13-R4DQNAT. (right) Western blot analysis of in vitro glycosylation reaction using purified scFv13-R4DQNAT acceptor protein that was incubated with purified CjPglB and organic solvent-extracted (solv-ext) CjLLOs. Control reactions (lane 1 in each panel) were performed by omitting purified CjPglB. b (left) Western blot analysis of scFv13-R4DQNAT produced by crude CLM24 extract selectively enriched with CjPglB from heterologous overexpression from pSF-CjPglB. (right) Western blot analysis of scFv13-R4DQNAT produced by crude CLM24 extract selectively enriched with CjLLOs from heterologous overexpression from pMW07-pglΔB. Reactions were primed with plasmid pJL1-scFv13-R4DQNAT and supplemented with purified CjPglB and organic solvent-extracted (solv-ext) CjLLOs as indicated. Control reactions (lane 1 in each panel) were performed by omitting solv-ext CjLLOs in (left) or purified CjPglB (right) in (b). Blots were probed with anti-hexa-histidine antibody (anti-His) to detect the acceptor protein or hR6 serum (anti-glycan) to detect the N-glycan. Arrows denote aglycosylated (g0) and singly glycosylated (g1) forms of scFv13-R4DQNAT. Molecular weight (MW) markers are indicated at left. Results are representative of at least three biological replicates
