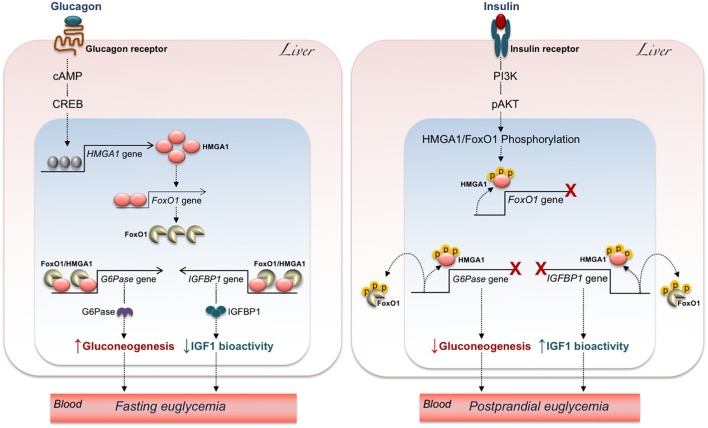
Figure 3.
Hypothetical mechanisms underlying the effects of HMGA1/FoxO1 on glucose homeostasis. The increase of glucagon during fasting (Left) turns on the cAMP-PKA-CREB pathway, allowing HMGA1 gene activation and protein expression. In turn, HMGA1 activates the FoxO1 gene and promotes transactivation of G6Pase and IGFBP1 promoters by FoxO1, thereby maintaining fasting euglycemia through elevation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and attenuation of IGF1 bioactivity. Under feeding conditions (Right), binding of insulin to its receptor initiates a series of events culminating in the sequential phosphorylation (p) of HMGA1 and FoxO1, which reduces FoxO1 gene expression, promotes the detachment of FoxO1 from G6Pase and IGFBP1 gene promoters, and leads to FoxO1 nuclear exclusion, thereby ensuring postprandial euglycemia through inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis and augmentation of IGF1 bioactivity.