Figure 2. CD8‐Lck coupling is a limiting factor for the size of the virtual memory T‐cell compartment.
-
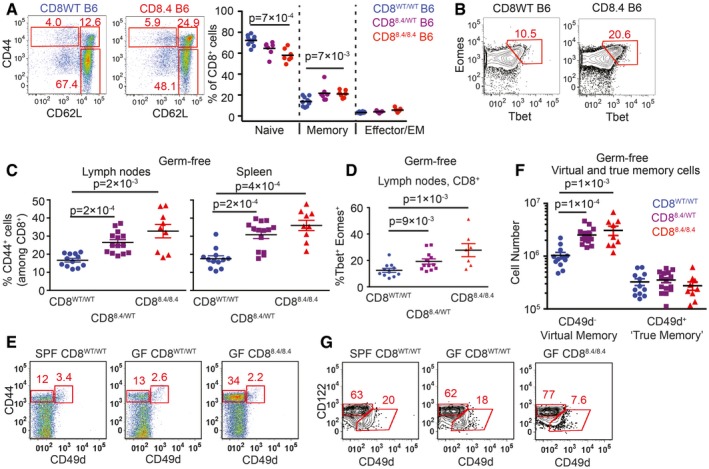
A, BPercentages of naïve (CD44− CD62L+), central memory (CD44+ CD62L+), and effector/effector memory (CD44+ CD62L−) (A) and Eomes+ Tbet+ (B) CD8+ LN T cells isolated from CD8WT and CD8.4 mice were determined by flow cytometry. Representative experiments out of seven (A) or five (B) in total.
-
C–FLN cells and splenocytes were isolated from germ‐free polyclonal CD8WT, CD8.4, and heterozygous CD8WT/8.4 mice and CD8+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Percentage of CD44+ T cells among CD8+ LN cells and splenocytes. Mean + SEM. n = 9–14 mice per group from four independent experiments. (D) Percentage of Tbet+ Eomes+ double‐positive T cells. Mean ± SEM. n = 7–12 mice per group from three independent experiments. (E) Percentage of CD44+ CD49d− VM and CD44+ CD49d+ true memory T cells in the spleen. A representative experiment out of four in total. (F) Absolute numbers of CD8+ CD44+ CD49d− VM and CD8+ CD44+ CD49d+ true memory T cells in LN and the spleen were quantified. Mean + SEM. n = 9–14 mice from four independent experiments.
-
GPercentage of CD122HI CD49d− VM and CD122LOW CD49+ true CM cells among CD8+ CD44+ CD62L+ CM T cells isolated from LN. A representative experiment out of three in total.
