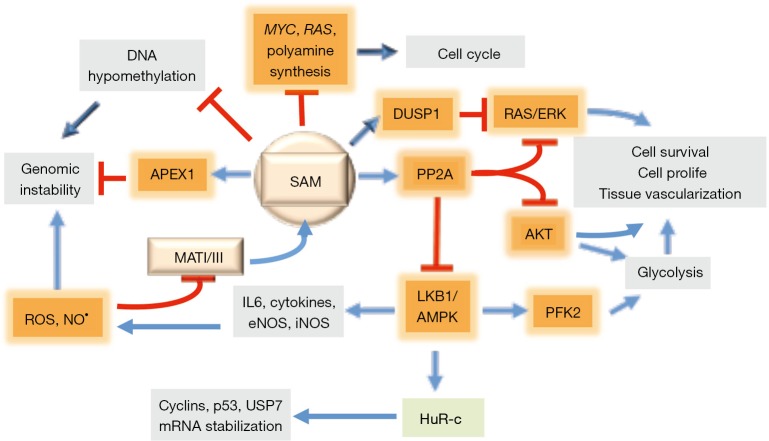
Figure 2.
Effects of SAM treatment during hepatocarcinogenesis. SAM is involved in DNA methylation and stabilization of the DNA repair enzyme APEX1. SAM antioxidant activity reduces genomic instability. The inhibition by SAM of LKB1/AMPK axis increases cytoplasmic concentration of HuR, which stabilizes p53 and USP7 mRNAs. Through the control of the LKB1/AMPK axis, SAM impedes the production of IL6 and cytokines and the activation of iNOS and eNOS, thus limiting the oxidative damage. SAM also controls cell growth and survival by inducing PPA2 expression that phosphorylates and inactivates AKT and its targets. Moreover, PPA2 activation and DUSP1 stabilization inhibit RAS/ERK pathway. Finally, SAM affects cell cycle by inhibiting c-MYC expression and polyamine synthesis. SAM, S-adenosylmethionine. Adapted with permission from Frau et al., 2013.