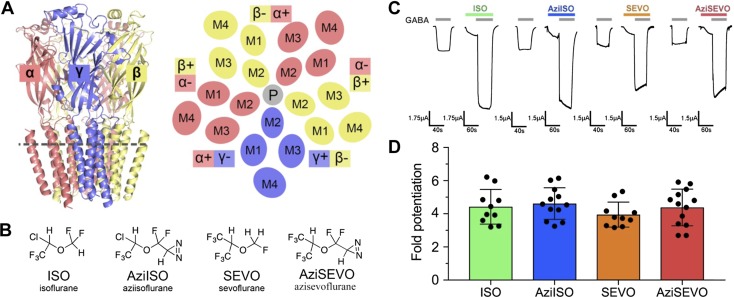
Figure 1.
ISO, AziISO, SEVO, and AziSEVO α1β3γ2L GABAA receptor activity. A) Membrane view of the α1β3γ2 GABAA receptor homology model and schematic of the cross-section as indicated by the gray dashed line of the receptor transmembrane domain viewed from the synaptic cleft. Receptor is colored by subunit type (α1, salmon; β3, yellow; and γ2, slate), and membrane-spanning helices (M1–M4) are labeled accordingly for each subunit. The plus and minus subunit interfaces are indicated for each subunit, and the pore (P) is indicated as a gray circle. B) Chemical structures of volatile anesthetics and their photolabel analogs. C) Representative traces of evoked current by GABA EC10 control and after combined GABA EC10 and 0.3 mM ISO, AziISO, SEVO, and AziSEVO exposures within individual X. laevis oocytes expressing the α1β3γ2L GABAA receptor. D) Fold potentiation of GABA EC10 by 0.3 mM ISO, AziISO, SEVO, and AziSEVO within X. laevis oocytes expressing the α1β3γ2L GABAA receptor. Data were analyzed by Mann–Whitney U test that compared the evoked currents of the parent anesthetic with the corresponding photolabel analog. No significant differences were observed.