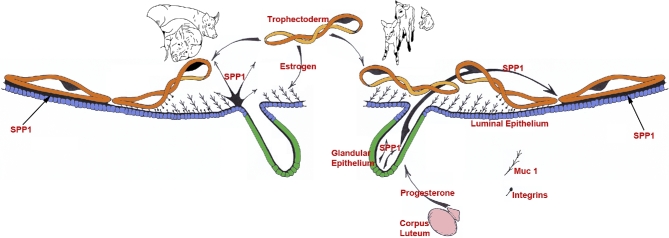
Figure 3.
Expression, regulation, and proposed functions of SPP1 produced by the uterine epithelia of pregnant pigs and sheep. Center to left: as porcine conceptuses (trophectoderm) elongate they secrete estrogens for pregnancy recognition. These estrogens also induce the synthesis and secretion of secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1 or osteopontin [OPN]) from the uterine LE directly adjacent to the conceptus undergoing implantation. The implantation cascade is initiated when progesterone from CL downregulates Muc 1 on the surface of uterine LE. This exposes integrins on the uterine LE and conceptus trophectoderm cell surfaces for interaction with SPP1, and likely other ECM proteins, to mediate adhesion of conceptus trophectoderm to uterine LE for implantation. Center to right: as the lifespan of the CL is extended due to the actions of IFNT secretion from elongating ovine conceptuses they secrete progesterone. Progesterone then induces the synthesis and secretion of SPP1 from the uterine GE. The implantation cascade is initiated with downregulation of mucin 1 (Muc 1) (the regulatory mechanism remains to be identified) on the uterine LE surface to expose integrins on the LE and conceptus trophectoderm cell surfaces for interaction with SPP1 to mediate adhesion of conceptus trophectoderm to uterine LE for implantation.