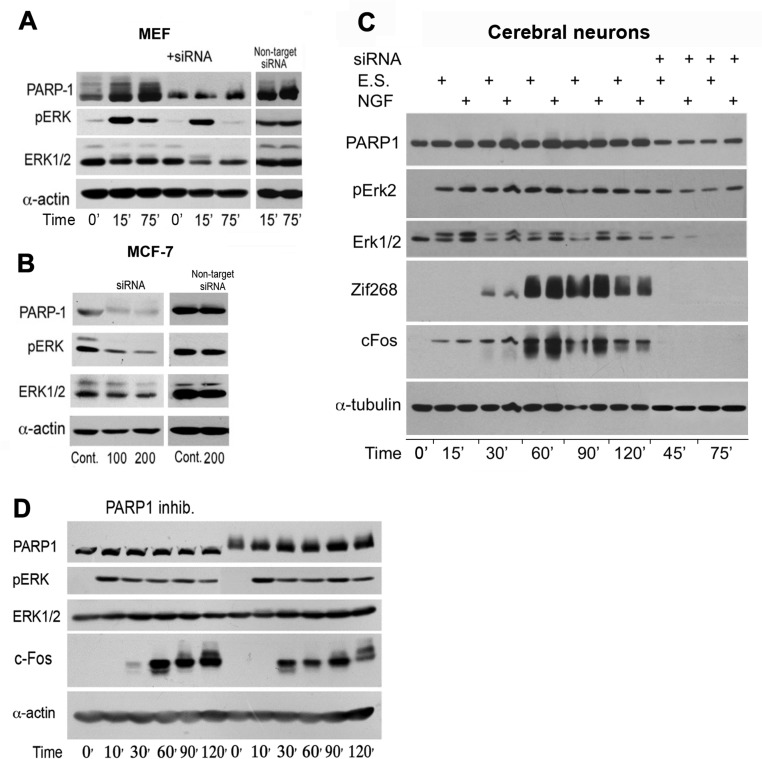
Figure 3. PARP1 mediates stimulation-induced Erk phosphorylation in the nucleus.
(A) PARP1 and phosphorylated Erk1/2 were monitored by immunolabeling during 120 min in MEF after stimulation with PMA (200 nM, 15 min). PARP1-silencing suppressed stimulation induced Erk phosphorylation in the nuclei of MEF and in nuclei of unstimulated human breast cancer MCF-7 cells (B). (C) PARP1, phosphorylated Erk1/2 and transcription factors c-Fos and Zif268 were monitored by immunelabeling during 120 min in cerebral cortical neurons after electrical stimulation (ES; 100 Hz, 1 sec, 3 repeats each followed by 10 sec pause), without or in the presence of nerve growth factor (NGF; 60 ng/ml, 5 min). Erk2 phosphorylation and proteins' zif 268 and c-Fos were hardly detected after PARP1 silencing. (D) PARP1 activity mediating Erk activity in MEF. A reversible inhibition of PARP1 in MEF treated with PJ34 (10 μM, 30 min) prior to PMA stimulation (200 nM, 20 min) prevented the following elevation of cFos (30 min after stimulation). Representative results of 3 different experiments are displayed for each of these experiments.