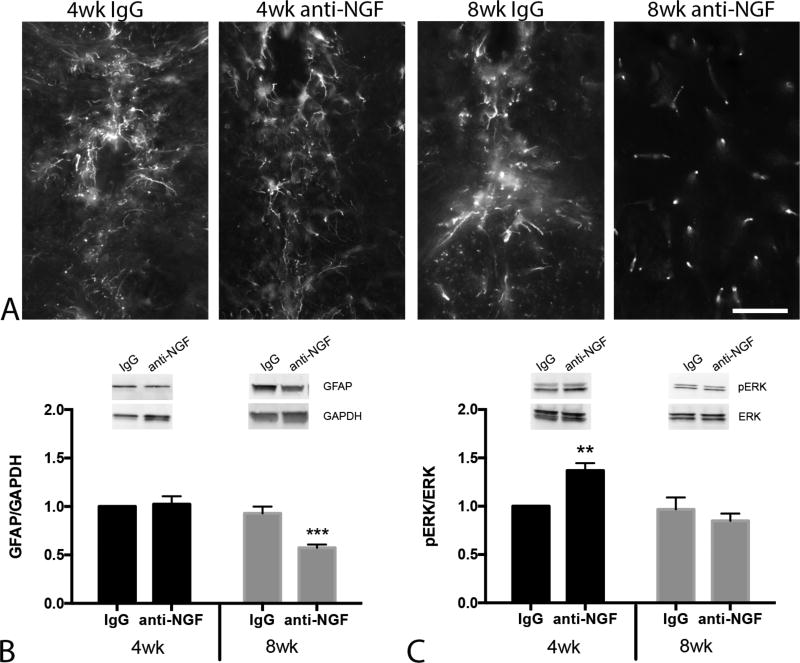
FIGURE 2.
Anti-NGF treatment reduces levels of the inflammatory marker GFAP in the thoracic spinal cord. A, High power micrographs show astrocyte morphology and GFAP immunoreactivity in the central canal region of the thoracic spinal cord across experimental groups. Note the lack of ‘activated’ astrocyte morphology in 8 wk treatment group. B, Western blots confirm reduced GFAP expression in 8 wk treatment group. Inset: Representative blot compares relative GFAP expression in IgG and anti-NGF treated mice. Band densities were normalized to GAPDH level. C, Mice that began anti-NGF at 4 wk of age exhibited significantly higher p-ERK expression. Inset: Representative western blot shows pERK expression (normalized to total ERK) in thoracic spinal cord. Immunoblot data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s test for multiple comparisons. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 n = 7–11/group. Scale bar in A =50µm.