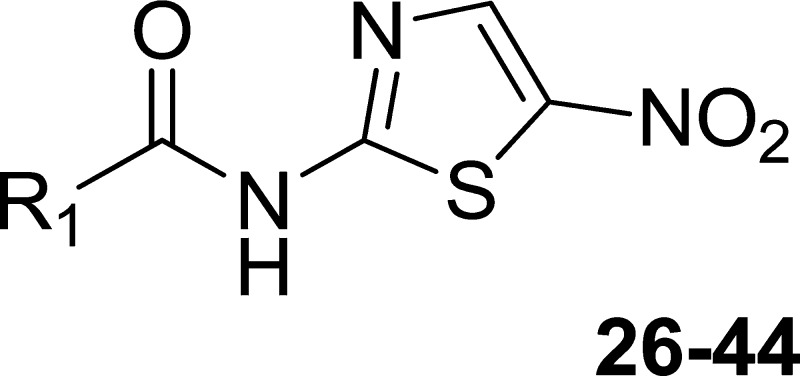
Table 2. SAR Studies of the Salicylate Region of 1.
| compound | R1 | MIC (μM) | TC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26 | methyl | >20 | >50 |
| 27 | cyclopropyl | >20 | >50 |
| 28 | cyclohexyl | >20 | >50 |
| 29 | 2-(OH)cyclohexyl | >20 | 37 |
| 30 | 4-pyrimidinyl | >20 | >50 |
| 31 | 1-piperidinyl | >20 | >50 |
| 32 | 2-pyrazinyl | >20 | >50 |
| 33 | 2-thiazolyl | >20 | >50 |
| 34 | 3-pyridyl | >20 | >50 |
| 35 | 4-pyridyl | >20 | >50 |
| 36 | 1-naphthylNH– | 17 ± 3.0 | >50 |
| 37 | PhNH– | 17 ± 4.2 | 7.0 |
| 38 | cyclohexylNH– | >20 | 6.1 |
| 39 | 2-pyridylNH– | >20 | 17 |
| 40 | 2-(1-methylimidazolyl) | >20 | >50 |
| 41 | 2-oxazolyl | >20 | >50 |
| 42 | 3-isoxazolyl | >20 | >50 |
| 43 | 2-(5-methylthiazolyl) | >20 | 18 |
| 44 | benzothiazolyl | >20 | 32 |
Compounds were tested for activity against M. tuberculosis. MIC (in μM) is the minimum concentration required to inhibit the growth of M. tuberculosis in liquid culture. MICs of active compounds are the average ± standard deviation of two independent experiments.
Toxic concentration (TC50, in μM) is the concentration required to inhibit growth of Vero cells by 50%.