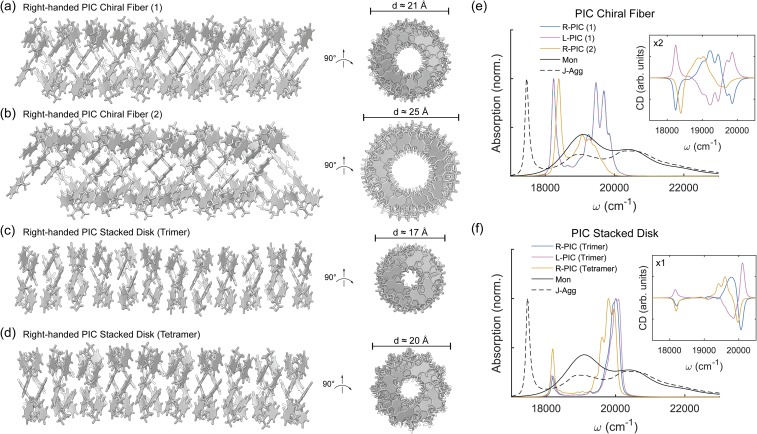
FIG. 4.
Chiral PIC superstructure models. (a) PIC right-handed linear aggregation using x = 1.2 Å, z = 3.7 Å, β = 180°, and γ = 78°, creating a rod-like superstructure with diameter d ≈ 21 Å. (b) PIC right-handed linear aggregation using two chiral threads of x = 1.2 Å, z = 3.8 Å, β = 180°, and γ = 60°, creating a rod-like superstructure with diameter d ≈ 25 Å. (c) PIC right-handed stacked disk superstructure where trimeric disks are built using x = 1.4 Å, y = 1.4 Å, z = 3.7 Å, β = 180°, and γ = 120°, with diameter d ≈ 17 Å. (d) PIC right-handed stacked disk superstructure where tetrameric disks are built using z = 3.7 Å, α = 10°, β = 180°, and γ = 90°, with diameter d ≈ 20 Å [(e) and (f)] Calculated PIC absorption and circular dichroic spectra for the right- and left-handed chiral and stacked aggregates compared to PIC monomer (Mon) and J-aggregated (J-Agg) spectra. Electronic couplings are calculated using the transition density cube (TDC) method from excited states calculated using TD-DFT [DFT-D3/B3LYP/6-31+G(d)] with implicit water solvation using COSMO. Site-basis Hamiltonians for each model are shown in Fig. S5 of the supplementary material.