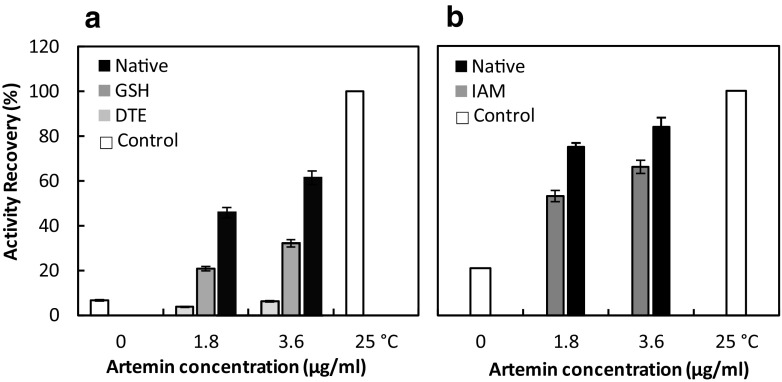
Fig. 2.
Assisted refolding of HRP (a) and CA (b) in the presence of various concentrations of reduced/modified and native artemin. The reducing reagents GSH and DTE cleave the disulfide bond of the chaperone, and the alkylation agent IAM blocks all reduced cysteine residues and prevents formation of the disulfide bond. The reduced and alkylated artemin were used to assess the recovery yield of denatured HRP (a) and CA (b), respectively. a The denatured HRP (1 mg/ml) was diluted to a final concentration of 0.0125 mg/ml using the appropriate refolding buffers containing different amounts of native artemin (black) and reduced artemin in the presence of GSH 10 mM (dark gray) and DTE 30 Mm (light gray) at 25 °C. b The denatured CA (10 mg/ml) was diluted to a final concentration of 0.2 mg/ml using the appropriate refolding buffers containing different amounts of native artemin (black) and modified artemin with IAM 100 mM (dark gray) at 25 °C. The residual activity of denatured HRP and CA was reported as the percentage recovery relative to the untreated enzymes (white) under similar experimental conditions. Results are the means for triplicate measurements