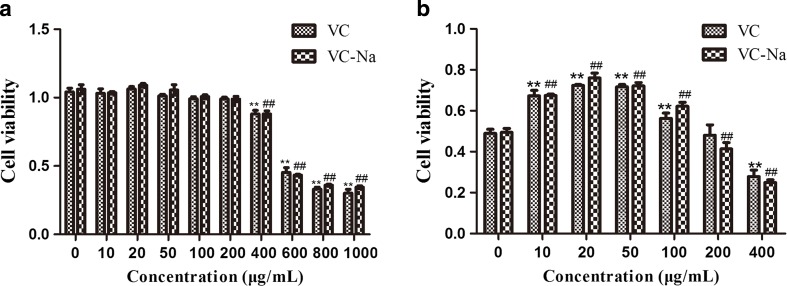
Fig. 1.
Viability of H9C2 cells. a Cell viability upon addition of various concentrations of vitamin C (VC) and vitamin C-Na (VC-Na) without heat stress. Addition of 200 μg/ml vitamin C and vitamin C-Na had no effect on H9C2 cells, but 400 μg/ml reduced cell viability. b Cell viability upon addition of various concentrations of VC and VC-Na following heat stress for 5 h. Addition of between 10 and 100 μg/ml increased cell viability, but 20 μg/ml resulted in the largest increase (~ 1.5-fold). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01compared with 0 h in the control group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 means supplements group compared with the control group or compared between the two supplements at the same timepoint