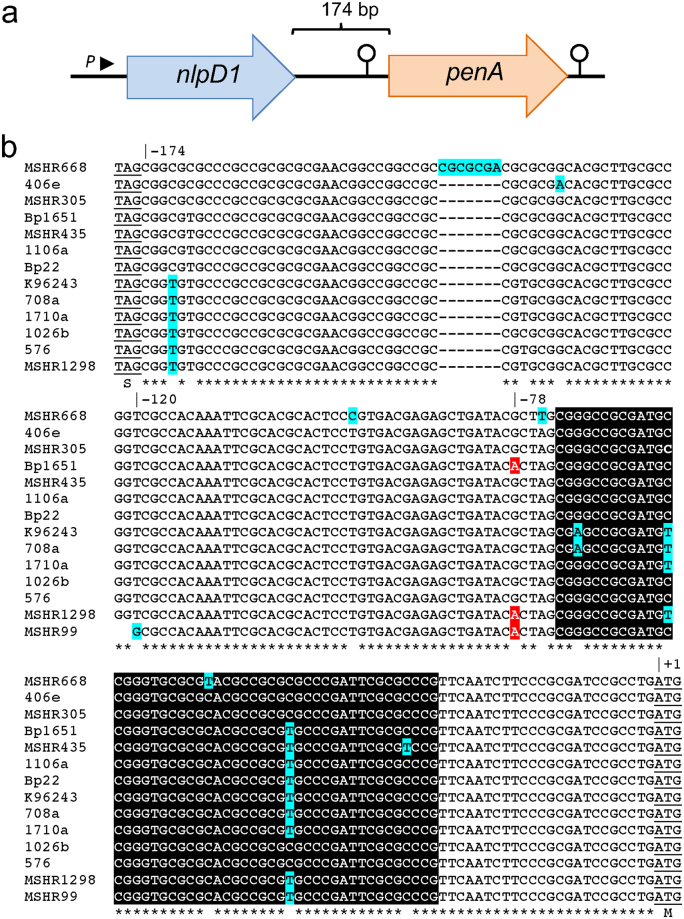
Figure 1.
Organization of the B. pseudomallei penA region on chromosome 2. (a) Map of the penA region with pertinent features. Wild-type strains contain no recognizable promoter in the 174 bp penA upstream region, only a predicted promoter (P) upstream of nlpD1. This arrangement suggests that nlpD1 and penA form an operon. Lollipop structures indicate proposed transcriptional terminators. The nlpD1 gene encodes a lipoprotein with homology to E. coli cell wall hydrolytic amidase activating NlpD. (b) Sequence of the nlpD1-penA intergenic region of selected strains. Of the indicated strains of mostly Australian and Thai origin, only Bp1651, MSHR1298 and MSHR99 are known to be CAZ resistant. All sequences except MSHR99 represent complete nlpD1-penA intergenic regions. The publicly available MSHR99 sequence extends to position −120 relative to the first nucleotide of the ATG start codon. Asterisks indicate identical nucleotides and variable nucleotides are shaded in turquoise, including a 7 bp insertion in MSHR668. The A nucleotides present at position −78 in the Bp1651, MSHR1298 and MSHR99 sequences are highlighted in red. (Note: Due to an outdated and mistaken annotation of the penA translational start site in several sequenced reference strains some of the literature refers to the G to A transition at position −21A.) Nucleotides located between −73 and −25 forming a proposed transcriptional terminator upstream of penA are boxed in black.