Fig. 2|. Typhoid toxin has in vivo tropism to endothelial cells of arterioles in the brain and to immune cells.
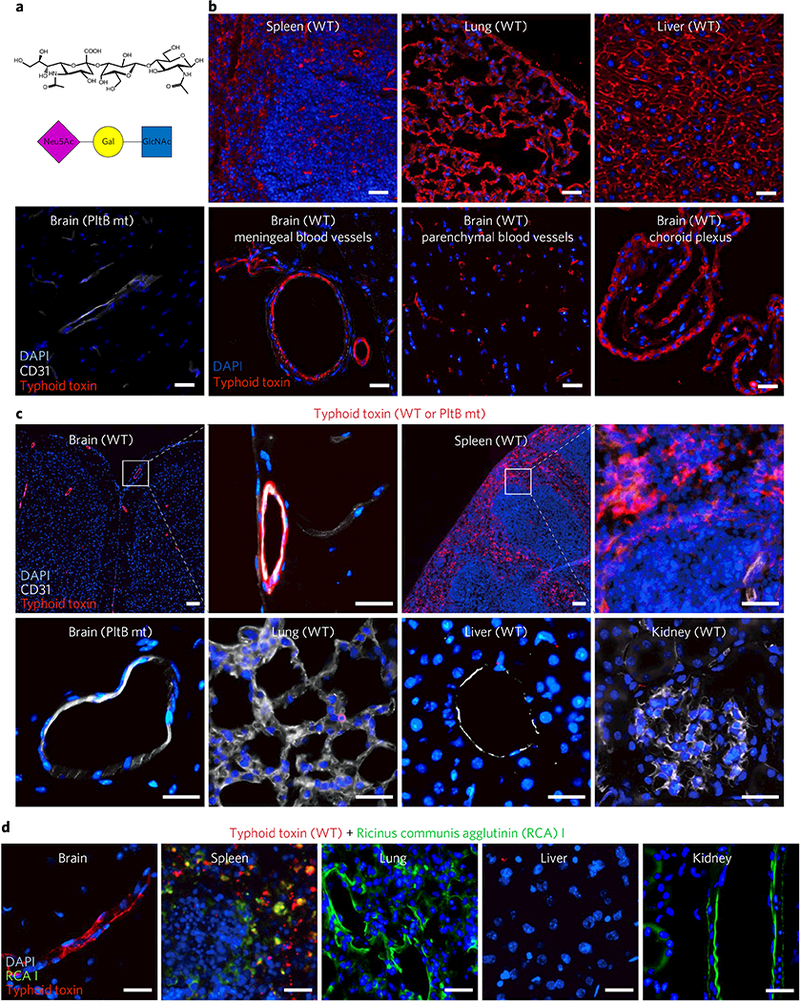
a, A schematic showing the trisaccharide consensus recognized by typhoid toxin PltB9–15. Neu5Ac, N-acetylneuraminic acid; Gal, galactose; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine. b, Visualization of the expression of the typhoid toxin glycan receptor (red). To investigate receptor expression, the indicated mouse tissue sections of untreated C57BL/6 mice were probed for Alexa555-conjugated typhoid toxin (n = 3) or Alexa555-conjugated PltB-binding-defective mutant (n = 3). Scale bar, 100 μm. These results indicate that the glycan receptor for typhoid toxin is ubiquitously expressed in the tissue sections tested. Images shown are representative of 30 images in at least three independent experiments. c, Alexa555-conjugated typhoid toxin (red), either WT toxin (n = 5) or a PltB binding defective mutant toxin (n = 3), was systemically administered into live C57BL/6 mice and toxin localization in various tissues was investigated 2 h after administration. Typhoid toxin localized in the brain and the spleen but did not localize in lung, liver and kidney. CD31 is a specific cell surface marker for endothelial cells, while DAPI stains DNA. A PltB mutant toxin conjugated to Alexa555 was defective for the binding to the brain endothelial cells, indicating toxin signal is specific. Scale bar, 100 μm. d, Ricinus communis agglutinin I (RCAI) conjugated to FITC (green) that has binding specificity to terminal galactose was co-administered along with typhoid toxin-Alexa555 into live C57BL/6 mice (n = 2). RCAI localized in spleen, lung and kidney but not in brain and liver, supporting the specific in vivo trafficking of typhoid toxin. Images shown are representative of 30 images in at least two independent experiments. Scale bars, 100 μm.
