Fig. 4|. Vaccination of naive mice with genetically engineered inactive typhoid toxin or PltB subunit alone completely protects the mice against a lethal-dose toxin challenge.
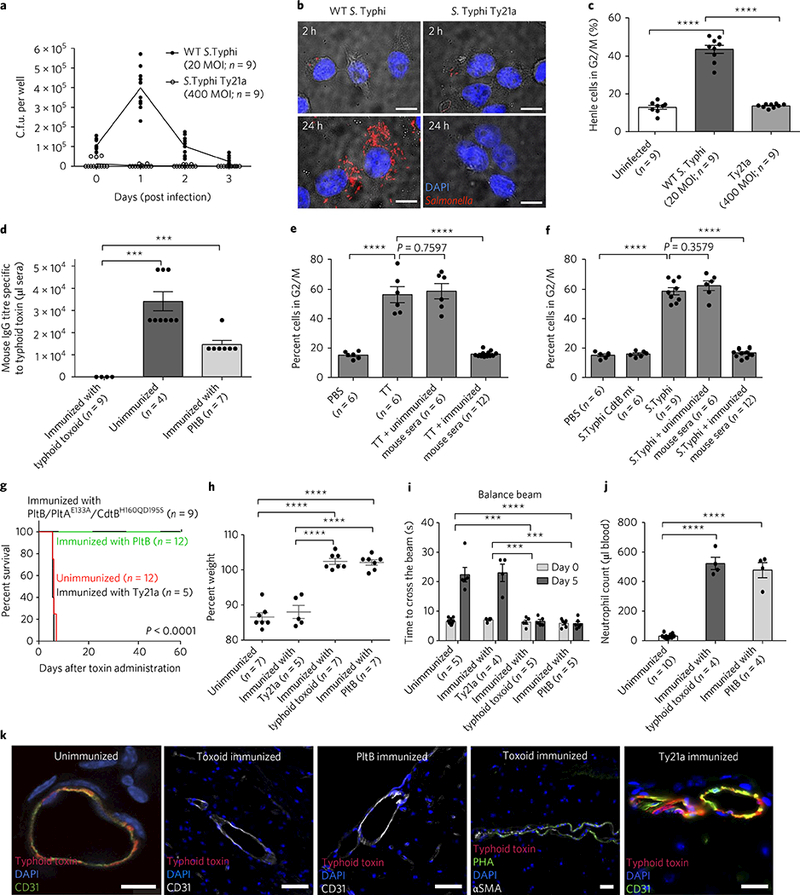
a-c, Determination of intracellular S. Typhi c.f.u. at indicated time points by plating (a) or fluorescent microscopy (b), and evaluation of typhoid-toxin-mediated toxicity of infected cells by flow cytometric cell cycle analysis 3 days after infection (c). The results indicate the limitations of S. Typhi Ty21a in producing typhoid toxin. Mice were immunized with typhoid toxoid, PltB pentamer or S. Typhi Ty21a, and PBS was used for the unimmunized control group. d, Relative serum antibody levels were determined by standard endpoint ELISA titration. e,f, Evaluation of typhoid-toxin-mediated toxicity (G2/M cell cycle arrest) in immunized sera-treated human cells. TT, WT typhoid toxin. In f, S. Typhi CdtB catalytic mutant (producing CdtB mutant typhoid toxin during infection, an experimental control) or WT S. Typhi (producing WT typhoid toxin) was used as a source of typhoid toxin. g-j, Both immunization strategies— with either typhoid toxoid (all three subunits) or PltB alone—efficiently protected mice against a lethal-dose typhoid toxin challenge, as shown by survival (g), no weight loss (h), no neurological complications (i) and no immune-cell-associated symptoms (j). In contrast, Ty21a did not protect mice against a typhoid toxin challenge. Antibody titres of Ty21a-immunized mouse sera are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10. k, Brain images of vaccinated and toxin-challenged mice. Typhoid toxin’s in vivo tropism to the brain was observed in both Ty21a-vaccinated mice (n = 5) and PBS-treated mice (n = 3), but not typhoid toxoid- or PltB subunit-vaccinated mice (n = 3 each) (see Supplementary Fig. 11 for a quantitative analysis of images). Note that immunized mice expressed multiantennal N-glycans (PHA+): CD31 for endothelial cells (green or white); PHA lectins for multiantennal N-glycans; αSMA for smooth muscle cells; DAPI for DNA. Images shown in b and k are representative of the finding. Scale bars, 10μm (b) and 100μm (k). Unpaired Student’s f-test was used for c-f and h-j (***P< 0.001, ****p< 0.0001) and a low-rank test for g.
