Figure 8.
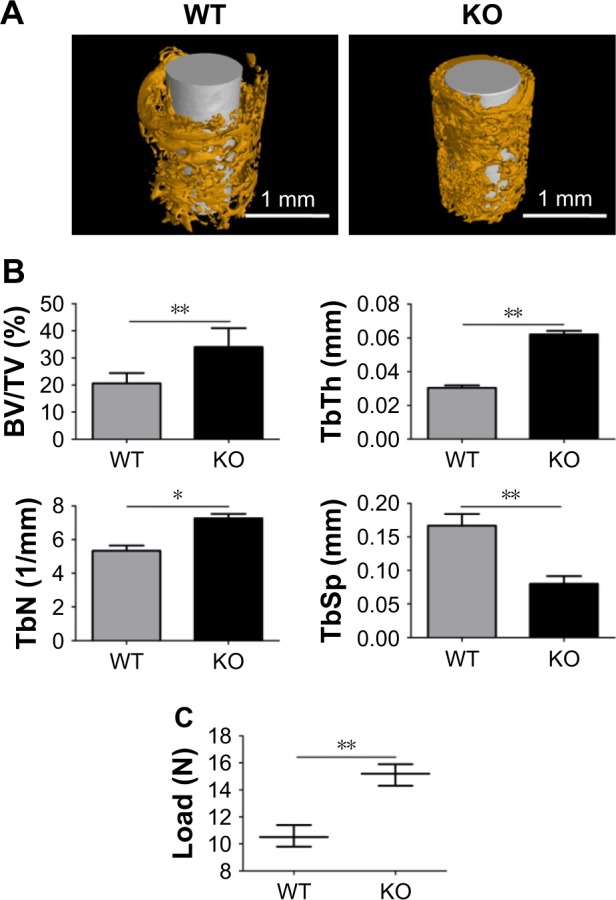
The effects of M1 polarization blocking on nanotopography-mediated osseointegration.
Notes: The titanium implants with the NT-100 surface were inserted in the femurs of WT mice and Cre*RBP-Jfl/fl (KO) mice of which the M1 macrophage polarization was blocked. Then, WT mice and KO mice were allowed to heal for 3 weeks. (A) Micro-computed tomography analysis of osteogenesis around the implants in WT mice and KO mice. (B) The ratio of BV/TV, TbTh, TbN, and TbSp in the region of interest of WT mice and KO mice were analyzed. (C) Analysis of push-in resistance of implants in WT mice and KO mice. Means were compared with one-way analysis of variance combined with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
Abbreviations: BV/TV, bone volume to total volume; KO, knockout; NT-30, titanium nanotube anodized under 5 V; NT-100, titanium nanotube anodized under 20 V; TbN, trabecular thickness; TbSp, trabecular separation; TbTh, trabecular thickness; WT, wild-type.
