Figure 3. K+ depolarization evokes Ca2+ signals in labelled pancreatic neurons.
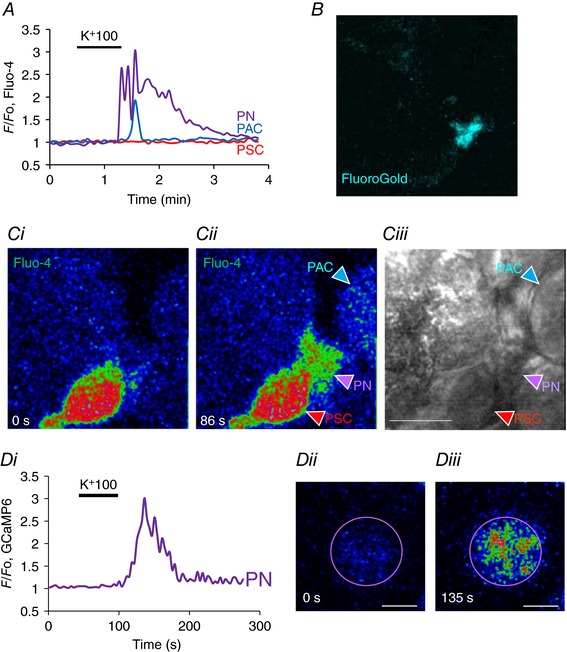
A, K+ depolarization evoked a rise in [Ca2+]i in a FluoroGold labelled PN (B) as well as in a PAC. Ci–ii, fluorescence images before (0 s) and during the high K+ challenge (86 s) showing the evoked rise in [Ca2+]i in the PN as well as the PAC, but with no change in the PSC. Ciii, transmitted light image of the field, also showing location of the different cells. Length of horizontal bar corresponds to 10 μm. D, ultrasensitive protein calcium sensor GCaMP6 was expressed in mouse pancreas by intravenous injection of adeno‐associated virus AAV9.Syn.GCaMP6s (Penn Vector Core at University of Pennsylvania) targeted to neurons. K+ depolarization evoked a significant rise in [Ca2+]i (Di). As seen in Dii, at rest the PN had relatively low fluorescence (0 s) but this increased by a factor of three after depolarization with high‐K+ solution (Diii, 135 s). Length of horizontal bars in Dii and Diii corresponds to 5 μm. No other cells in the field of view displayed any changes in fluorescence intensity. In this experiment the only fluorescent probe present was GCaMP6.
