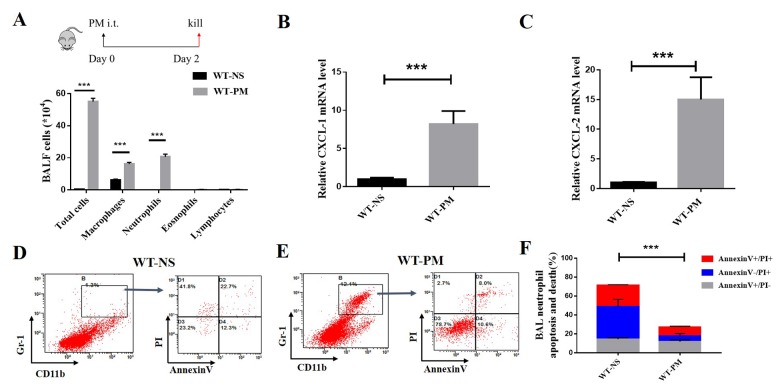
Figure 1.
PM-induced lung inflammation is dominated by neutrophil accumulation, and PM reduced the apoptosis of neutrophils in BALF. We established a PM-induced lung inflammation model with instillation of PM at 100 μg/d/mouse for 2 days in WT mice (n=5 to 7 per group). PM increased the total number of macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes in BALF. (A) Inflammatory cytokines such as the mouse chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL-1) and CXCL-2 were significantly increased in WT-PM mice (B and C). Apoptosis in neutrophils were determined by Annexin V and PI staining based on the gating of Gr-1+/CD11b+ by flow cytometry. PM decreased the apoptosis of neutrophils in BALF cells (D-F).