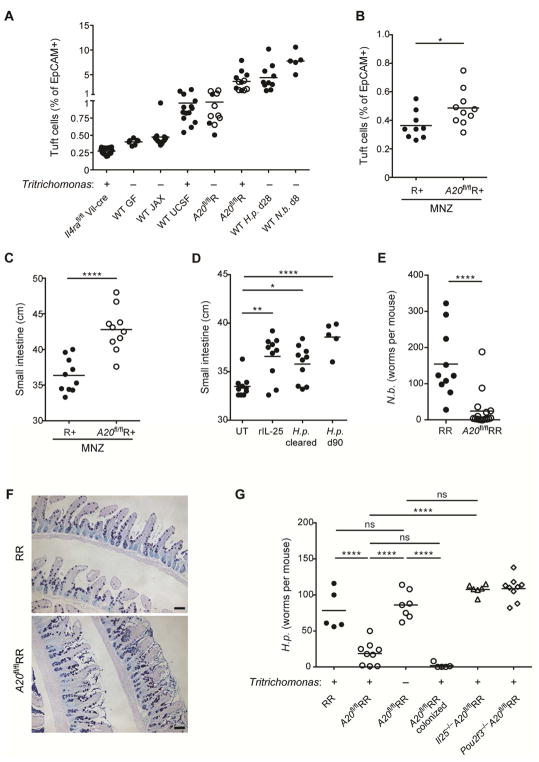
Figure 7. The tuft cell – ILC2 circuit contributes to concomitant immunity.
(A) Small intestinal (SI) tuft cell frequencies in indicated mice with presence (+) or absence (−) of Tritrichomonas as indicated. Some data is repeated from previous figures for comparison. Wild-type (WT) mice as in Fig. 5: JAX, offsprings of mice from JAX; UCSF, offsprings of mice colonized with Tritrichomonas. A20flR pooled from A20flR+ (open circle) and A20flRR (closed circle) mice. WT mice analyzed at indicated time points after infection with H. polygyrus (H.p.) or N. brasiliensis (N.b.). (B and C) Adult R+ and A20flR+ mice treated with metronidazole (MNZ) in drinking water for 2 weeks and frequencies of tuft cells (B) and SI length (C) analyzed. (D) WT mice serially treated with rIL-25 or infected with H. polygyrus (H.p.) for 4 weeks followed by worm clearance (cleared) in indicated mice using pyrantel pamoate. SI length measured 2 months after the last rIL-25 administration or worm clearance. (E and F) Worm burden (E) and Alcian blue/PAS staining (F) in SI of RR and A20flRR mice 5 days after infection with N. brasiliensis. (G) SI worm counts of indicated mouse strains 13 days after infection with H. polygyrus. Presence (+) or absence (−) of Tritrichomonas indicated. One group of Tritrichomonas-free A20flRR mice was colonized with Tritrichomonas 2 weeks before the infection. Data pooled from multiple independent experiments (A–E) or from one experiment representative of at least two independent experiments (F, G).*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant by Mann-Whitney U or one-way ANOVA.