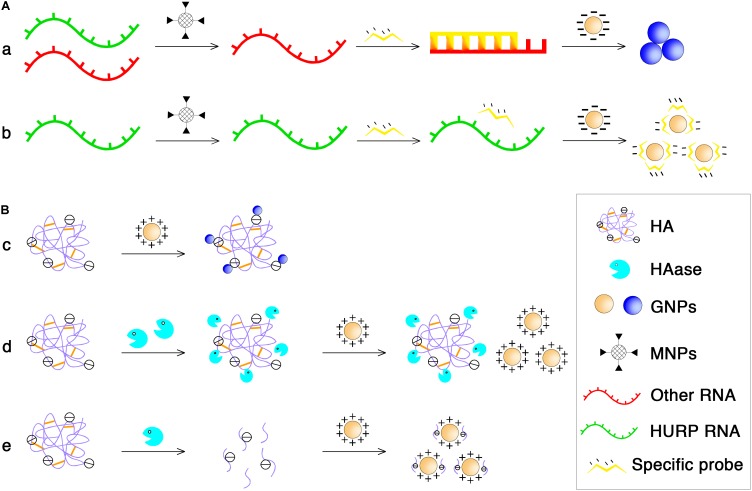
FIGURE 3.
The principle of NP-based diagnosis of BCa. (A) MNPs and GNPs used in purifying total RNA to obtain HURP RNA. (a) MNPs functionalized with oligonucleotide sequences specific for HURP RNA were added followed by mixing with hybridization buffer which contained NaCl, and HURP specific oligonucleotide with purified HURP RNA. After denaturation and annealing, the negatively charged GNPs were added and in the presence of HURP RNA, hybridization occured between the oligotargeter and the HURP RNA, and the solution color shifted from red to blue due to salt-induced aggregation of GNPs. (b) Without HURP RNA, GNPs would not aggregate and the solution color remained red because the oligotargeter remained adsorbed onto the surface of the GNPs. (B) Cationic GNPs directly detected HAase activity. (c) The charge interaction between polyanionic HA and cationic GNPs can lead to the formation of gold aggregates and at the same time a red to blue color shifted. (d) Under conditions of high HAase concentration, the enzyme and HA binds electrostatically even at a 0-min incubation time at 37°C, no aggregation occurs when the GNP solution is added, and the solution remains red in color. (e) At low concentration conditions, enzymatical reaction at 37°C for a period of time could lead to the enzyme molecule digest HA into small fragments, resulting in the failure of GNPs aggregation.