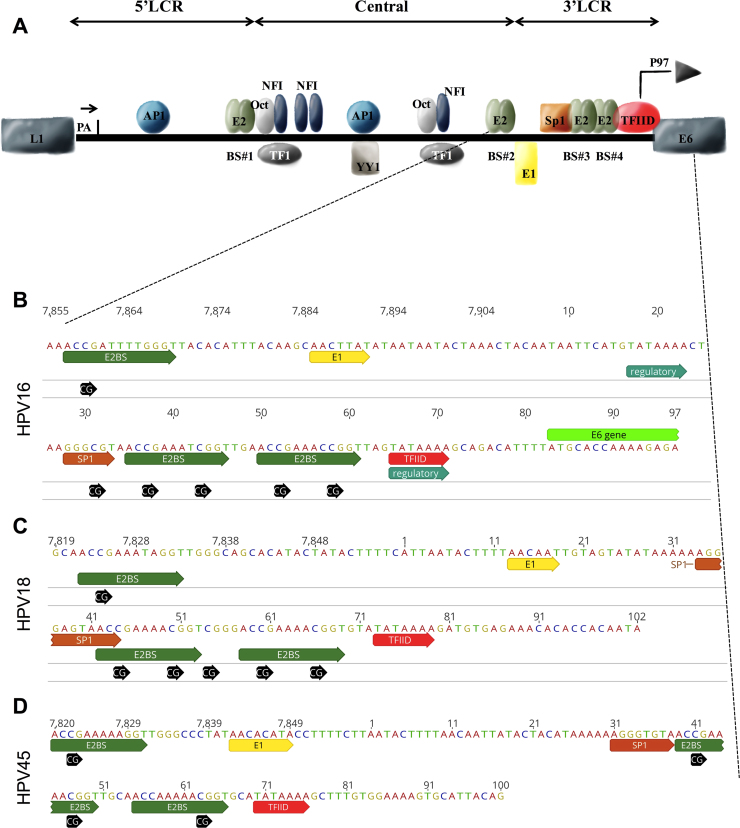
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of HPV LCR. A, represents the three segments of HPV16 LCR (5′LCR, central or enhancer, and 3′LCR), considered a model of LCR for all HPVs. The 5′LCR contains the transcription termination signal, denoted ‘pA’. The central segment contains the majority of transcription factor binding sites. The 3′LCR contains the origin of replication and the E6/E7 promoter. B, C and D, represent the nucleotide sequence of 3′LCR of HPV16, HPV18 and HPV45, respectively, highlighting the binding motifs of E2, E1, Sp1, TFIID and all CpG sites within this segment. The Sp1 motif of HPV16 contains one CpG site in its core (B, GGGCGT). Differently no CpG is found in the Sp1 motif of HPV18 (C, GGGAGT) and HPV45 (D, GGGTGT). The E2BS#4 of HPV45 (D) has only one CpG site (nt 63), while HPV16 (B) and HPV18 (C) contain two CpG sites. (For information on motifs and reference genome data see references [3], [40], [47] and Papillomavirus Episteme database [26], respectively). All transcription factor binding sites are denoted by the abbreviation used in the text except for TEF-1 that is herein denoted as TF1.