FIGURE 2.
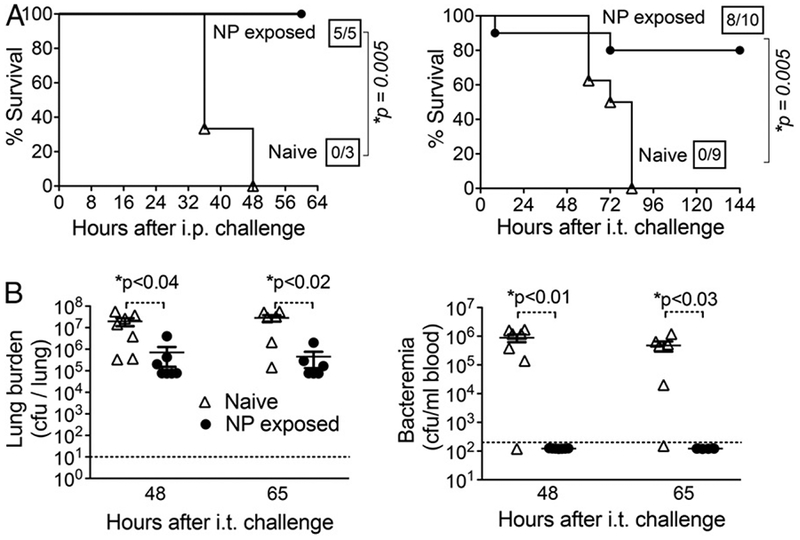
NP exposure results in protection against subsequent systemic challenge by S. pneumoniae. (A) After 3 wk of NP exposure to S. pneumoniae TIGR4, 8- to 10-wk-old C57BL/6 mice were challenged i.p. (left panel) with 100 CFU or i.t. with 1 × 107 CFU (i.t.; right panel) and survival was assessed. Boxed fractions denote survivors over total mice 2 wk after challenge. For i.t challenge, data pooled from two independent experiments are shown. (B) At the indicated times after i.t. challenge with 2 × 105 CFU of S. pneumoniae TIGR4, naive (n = 7) or NP-exposed (n = 6) mice were sacrificed and bacterial burdens in the blood (left) or lung homogenates (right) were determined. Dotted lines represent the limit of detection, and bars represent the mean. Points underneath the dotted lines illustrate that no bacteria were detected. For both panels, asterisks indicate significance calculated by a Student t test
