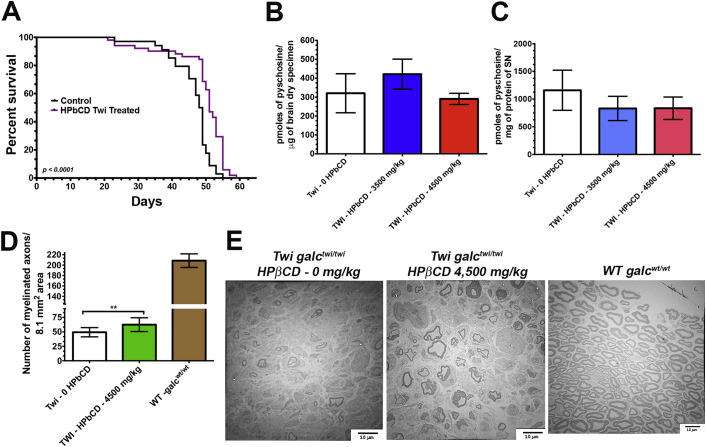
Fig. 1.
The effects of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) in the Twitcher mouse model for Krabbe disease. (A) Survival analysis of Twitcher (Twi galctwi/twi) mice treated with HPβCD (n = 34) and controls (n = 51). Equal number of males and females of Twi galctwi/twi were used in both groups. From post-natal day 3 until their death, treated Twi mice group received 4500 mg/kg of HPβCD subcutaneously diluted in phosphate saline every 2 days. An initial group of 12 mice receiving 3500 mg/kg subcutaneously also in the same frequency and duration are included in this survival analysis. Psychosine levels measured by LC-MS/MS in the brain (B) and sciatic nerve (C) specimens showed no statistically significant differences between mice receiving HCβCD (n = 6) and those receiving only saline (n = 6). (D) The number of myelinated axonal bulbs were significantly increased in the mice receiving HCβCD (n = 6) in comparison to controls (n = 6) (p < 0.05). (E) The transmission electron microscopy images of sciatic nerves dissected post-mortem showed increased preservation of myelinated fibers in the group of Twi mice receiving HPβCD.