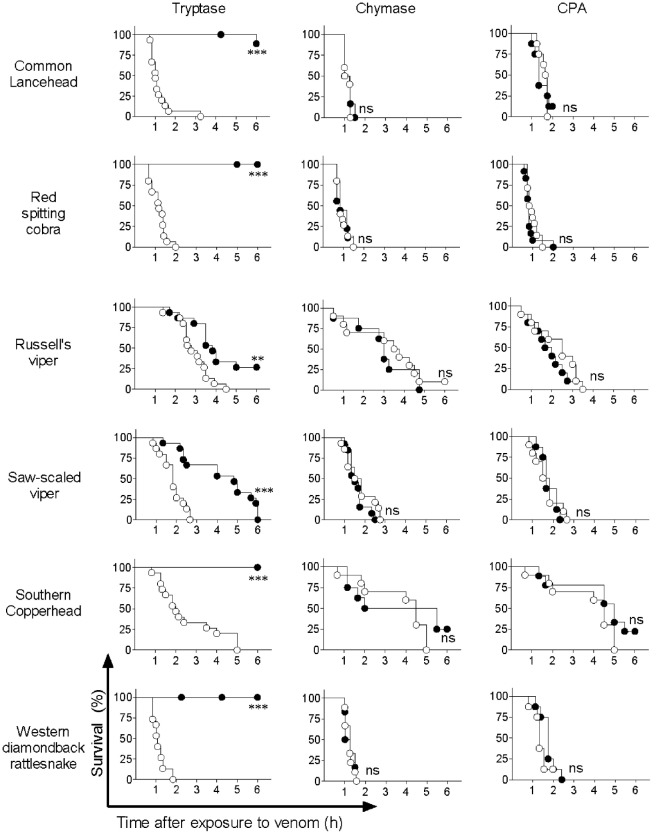
Figure 3.
Purified human tryptase, but not chymase or carboxypeptidase A (CPA), detoxifies snake venoms. Venoms were incubated with 10 µg/ml human tryptase, chymase, or CPA. Treated and untreated venom were then administered to 48 h post fertilization zebrafish in 100 µl of water. Empty circles represent zebrafish receiving venom alone, and solid shapes represent fish receiving enzyme-treated venom. Vehicle or enzyme alone had no effect (data not shown). Data are pooled from three (tryptase) or two (chymase and CPA) independent experiments for n = 15 or 10 fish per group. Kaplan–Meyer survival analysis, Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test compares treatments to vehicle. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.