FIGURE 2.
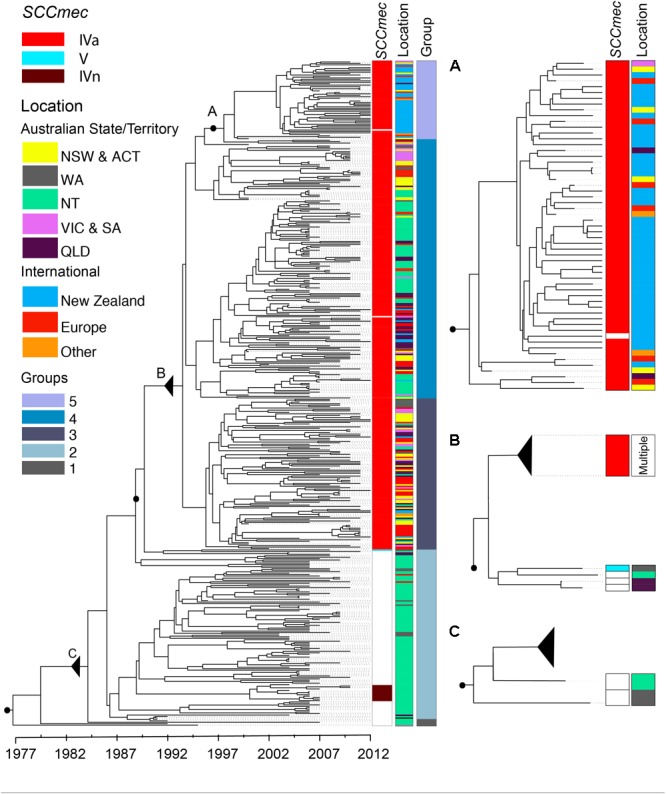
ST93 phylogeny. Maximum clade credibility tree obtained from the core genome not affected by recombination of 459 ST93 sequences using BEAST2. x-Axis depicts time in years. Metadata from left to right indicate the presence or absence of the mecA gene by SCCmec type (i.e., methicillin resistance; white – absence, red – SCCmecIVa, brown – SCCmecIVn, light blue – SCCmecV), the region of origin, and clustering based on the network analysis. Three regions of interest are magnified to the right of the tree with associated metadata. (A) Corresponds with group 5 containing predominantly isolates from New Zealand (see text for details). (B) Acquisition events of SCCmecIVa and SCCmecV elements leading to the establishment of ST93-MRSA-IVa. (C) The likely origin of ST93 showing the earliest basal strains of ST93-MSSA leading into the main MSSA group. Letters, black filled circles, and solid triangles (collapse point of the rest of the tree) allow for correlation of inserts with the total phylogeny. NZ, New Zealand; EU, Europe; NSW, New South Wales; NT, Northern Territory; QLD, Queensland; VIC, Victoria; WA, Western Australia. Australian Capital Territory (n = 1) and South Australian (n = 2) isolates are included with NSW and Victorian isolates, respectively.
