Extended Data Figure 2. Effect of constitutive BRAFV600E expression in Csf1r-expressing cells.
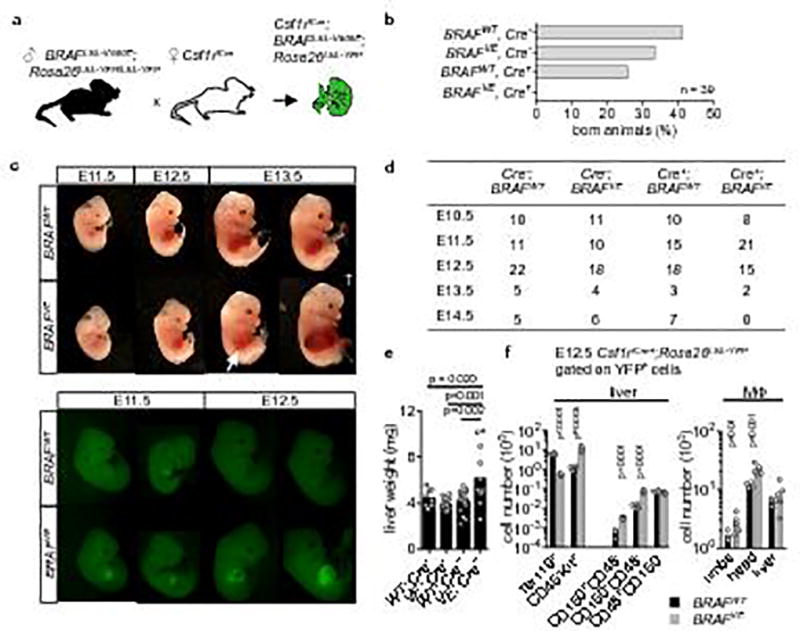
(a) Breeding scheme. (b) Embryonic lethality of Csf1riCre+; BRAFLSL-V600E; Rosa26LSL-YFP mice, bars represent the % of mice born from the cross depicted in (a) according to their genotype (n=39). (c) Brightlight (upper panel) and epifluorescence microscopy (lower panel) of Csf1riCre+ BRAFVE and Csf1riCre+; BRAFWT embryos showing haemorrhagic foci in the liver (arrow) and accumulation of YFP+ cells in fetal liver. † indicates dead embryo. Pictures are representative of n=3 per genotype. (d) Mouse embryos found alive during different developmental stages. Csf1riCre+; BRAFLSL-V600E; Rosa26LSL-YFP mice are associated with 100 % lethality beyond E14.5. (e) Liver weight of E12.5 embryos. Circles represent individual mice. n=8 for WT; Cre−, n=14 for VE; Cre−, n=16 for VE; Cre−, n=12 for VE; Cre+. One-way ANOVA. (f) Flow cytometry analysis of Lin− Kit+ blast, erythroid cell (Ter119) and hematopoietic stem cell numbers (LSK CD150+CD48− and CD150−CD48−) in the E12.5 fetal liver and of E12.5 tissue-resident macrophages in the limbs, head and liver. Circles represent individual mice. n=4 for BRAFWT and n=6 for BRAFVE. Unpaired two-tailed t-test.
