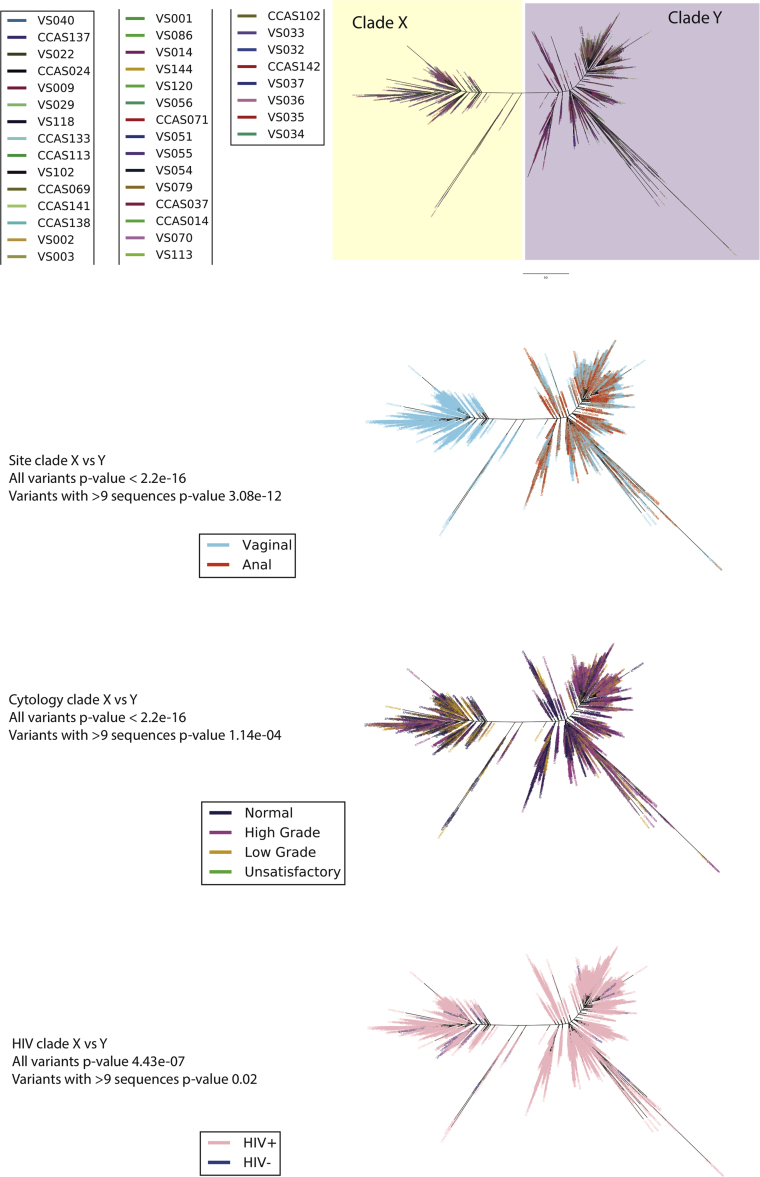
Fig. 4.
HPV 16 phylogenetic tree was constructed from 38 samples from 34 women and a total of 4275 variants using maximum likelihood (RAxML). The best tree was created from four multiple runs and 10,000 boot-straps and presented in ‘Fan’ mode. Two clades (X and Y) are observed. The tree was colour based on four variables; A) sample, B) site (vaginal or anal), C) cervical cytology outcome and D) HIV status. Cytology outcome were encoded according to Bethesda classification; Negative = Negative = Negative for intra-epithelial lesions and malignancy (NILM), High grade = High = High grade squamous intra-epithelial lesions (HGSIL) and Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude HGSIL (ASC-H), Low grade = Low‐grade = Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LGSIL) and Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) and Unsatisfactory = slide = slide was not satisfactory for evaluation.