Figure 1.
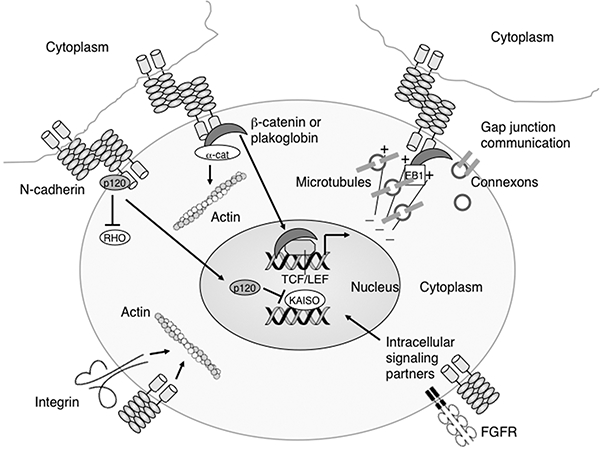
N-cadherin affects a range of biological activities. Schematic representation of the multiple functions of N-cadherin. Besides mediating cell-cell interactions between neighboring cells, N-cadherin may influence cell signaling by binding β-catenin, plakoglobin and p120 catenin thus regulating their ability to enter the nucleus and modulate gene expression. Additionally, unbound p120 can also regulate cell motility by inhibiting the activity of RHO GTPases. The forward trafficking of connexon-containing vesicles to the membrane is dependent on N-cadherin/β-catenin interactions with microtubule plus-end-tracking proteins, including EB1. N-cadherin stabilizes fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) at the membrane thus enhancing its downstream signaling pathways. N-cadherin and integrins cooperate to regulate actin dynamics important for cell motility.
