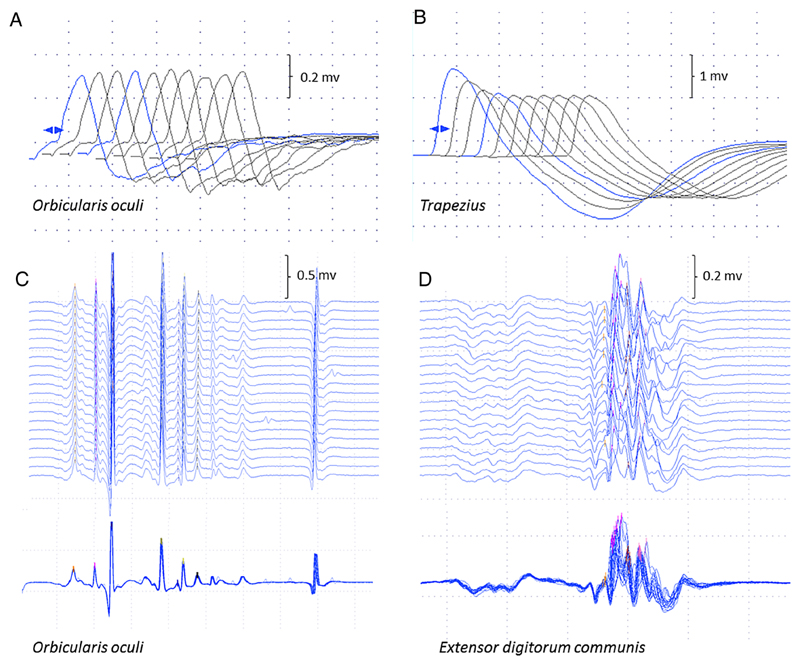
Figure 2.
Neurophysiological studies. Repetitive nerve stimulation in case 5 was normal in orbicularis oculi (A) compared to 25% decrement in trapezius (B) The stimulated SFEMG study of orbicularis oculi (C) was normal (mean consecutive difference 16.2 μs; 62% of the upper limit of normal) compared to the examination of extensor digitorum communis (D), which showed instability of the neuromuscular junction (mean consecutive difference 54.7 μs; 210% of the upper limit of normal), as seen in the superimposed traces. SFEMG, single fibre EMG.