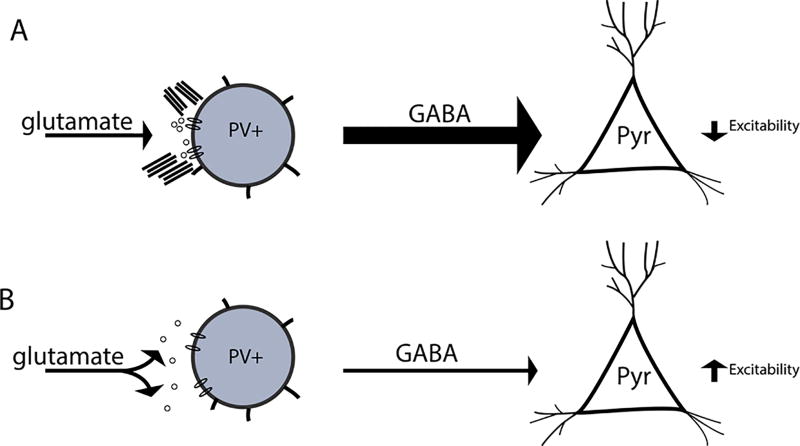
Figure 5.
Hypothetical model by which PNN disruption influences the frequency of SWR events. In figure 6 we show a hypothetical model. A PV neuron with an intact PNN is shown at the top left. This neuron receives spatially localized glutamatergic input, allowing it to in turn inhibit pyramidal cell excitability. In contrast, a PV neuron with a disrupted PNN is shown at bottom left. In this scenario, glutamate may more easily diffuse from the synaptic cleft and/or glutamate receptors may demonstrate enhanced lateral mobility. A potential result is that this PV is less activated and thus less able to inhibit pyramidal cell excitability.