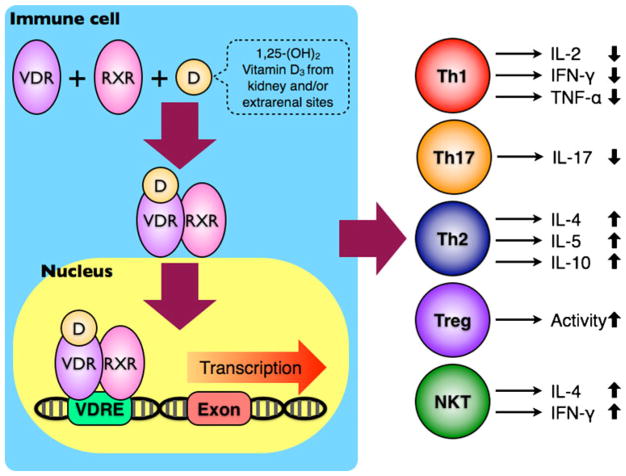
Fig. 2.
The immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D on immune cells. After binding to VDR, the biologically active 1,25-(OH)2 vitamin D3 can induce a conformational change on VDR and increase its affinity to RXR. The VDR-RXR heterodimer becomes a transcriptional factor, interacts with VDREs in the promoter regions of different genes, and ultimately leads to functional changes in multiple immune cell lineages, including Th1, Th17, Th2, Treg, and NKT cells