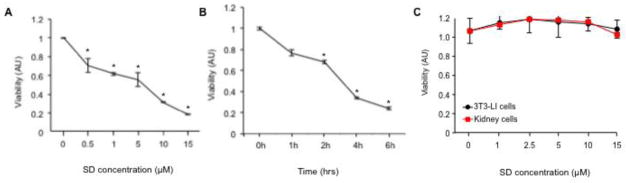
Figure 1. SD are cytotoxic to neuroblastoma cells but not non-malignant cells.
(A) Dose response of SD-mediated cytotoxicity. Exponentially growing Kelly cells were exposed to a range of SD concentrations (0–15 μM). After 24 h incubation, cell viability was assessed by MTS assay. Results are presented as arbitrary units (AU). * P values: p < 0.001 for 0.5 μM; p = 0.02 for 1 μM; p < 0.001 for 5 μM; p = 2 x10−6 for 10 μM; p < 2 x 10−6 for 15 μM. The results shown are representative of three similar experiments; n = 3 for each point. (B) Time-dependent inhibition of viability in response to SD treatment. Exponentially growing Kelly cells were treated with 10 μM SD or vehicle and incubated for 0–6 h, and viability was determined by MTS assay. * P values: p < 0.02 for 2h; p = 1 x 10−5 for 4h; p = 3 x 10−7 for 6h. The results shown are representative of three similar experiments; n = 3 for each point. (C) NIH 3T3 fibroblasts and primary human kidney cells established as described in Methods were exposed to a range of SD concentrations from 0–15 μM. After 24 h, cell viability was assessed by the MTS assay. The results shown are representative of three similar experiments; n = 3 for each point. There is no significant difference in SD-treated vs. vehicle-treated NIH3T3 or kidney cells at any concentration.