Figure 2.
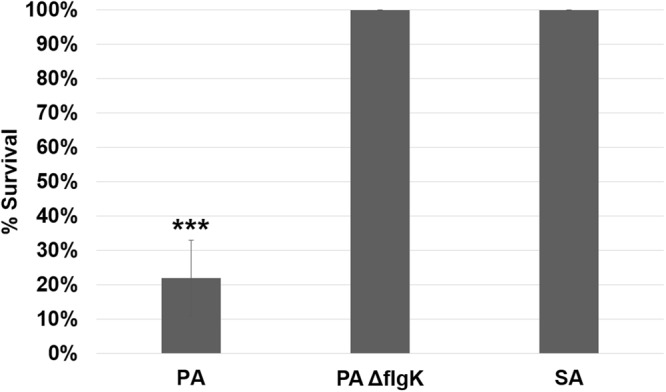
Swimming motility is required for dispersal-induced septicemia. Treatment of 48-hour mouse chronic wounds, infected with wild-type (PA) or a flagella mutant of P. aeruginosa, or with S. aureus (SA), with 10% α-amylase and cellulase (1:1; GH), resulted in ~80% septicemia only in mice infected with the motile strain. Repeated measures ANOVA and the Tukey-Kramer multiple-comparison test were used to test for differences between columns: ***p < 0.001. N = 9 for each group.
